The IFITM proteins inhibit HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 21177806
- PMCID: PMC3067758
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01531-10
The IFITM proteins inhibit HIV-1 infection
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2011 Apr;85(8):4043. He, Wei [added]
Abstract
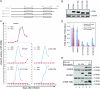
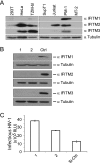
Type I interferon protects cells from virus infection through the induction of a group of genes collectively named interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). In this study, we utilized short hairpin RNA (shRNA) to deplete ISGs in SupT1 cells in order to identify ISGs that suppress the production of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Among the ISG candidates thus identified were interferon-induced transmembrane (IFITM) proteins, including IFITM1, IFITM2, and IFITM3, that potently inhibit HIV-1 replication at least partially through interfering with virus entry. Further mutagenesis analysis shows that the intracellular region, rather than the N- and C-terminal extracellular domains, is essential for the antiviral activity of IFITM1. Altogether, these data suggest that the IFITM proteins serve as important components of the innate immune system to restrict HIV-1 infection.
Figures
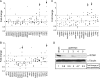
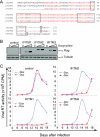
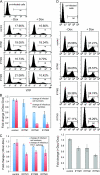


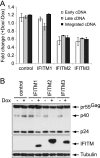

References
-
- Agy, M. B., R. L. Acker, C. H. Sherbert, and M. G. Katze. 1995. Interferon treatment inhibits virus replication in HIV-1- and SIV-infected CD4+ T-cell lines by distinct mechanisms: evidence for decreased stability and aberrant processing of HIV-1 proteins. Virology 214:379-386. - PubMed
-
- Andreu, P., et al. 2006. Identification of the IFITM family as a new molecular marker in human colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 66:1949-1955. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury, L. E., G. S. Kansas, S. Levy, R. L. Evans, and T. F. Tedder. 1992. The CD19/CD21 signal transducing complex of human B lymphocytes includes the target of antiproliferative antibody-1 and Leu-13 molecules. J. Immunol. 149:2841-2850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

