Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta is a target of enviroxime-like compounds for antipoliovirus activity
- PMID: 21177810
- PMCID: PMC3067798
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02249-10
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta is a target of enviroxime-like compounds for antipoliovirus activity
Abstract
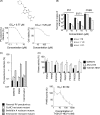
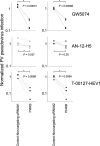
Enviroxime is an antienterovirus compound that targets viral protein 3A and/or 3AB and suppresses a step in enterovirus replication by unknown mechanism. To date, four antienterovirus compounds, i.e., GW5074, Flt3 inhibitor II, TTP-8307, and AN-12-H5, are known to have similar mutations in the 3A protein-encoding region causing resistance to enviroxime (a G5318A [3A-Ala70Thr] mutation in poliovirus [PV]) and are considered enviroxime-like compounds. Recently, antienterovirus activity of a phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase III beta (PI4KB) inhibitor, PIK93, was reported, suggesting that PI4KB is an important host factor targetable by antienterovirus compounds (N. Y. Hsu et al., Cell 141:799-811, 2010). In this study, we analyzed the inhibitory effects of previously identified enviroxime-like compounds (GW5074 and AN-12-H5) and a newly identified antienterovirus compound, T-00127-HEV1, on phosphoinositide (PI) kinases. We found that T-00127-HEV1 inhibited PI4KB activity with a higher specificity for than other PI kinases, in contrast to GW5074, which had a broad specificity for PI kinases. In contrast, AN-12-H5 showed no inhibitory effect on PI4KB activity and only moderate inhibitory effects on PI 3-kinase activity. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) screening targeting PI kinases identified PI4KB is a target of GW5074 and T-00127-HEV1, but not of AN-12-H5, for anti-PV activity. Interestingly, T-00127-HEV1 and GW5074 did not inhibit hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication, in contrast to a strong inhibitory effect of AN-12-H5. These results suggested that PI4KB is an enterovirus-specific host factor required for the replication process and targeted by some enviroxime-like compounds (T-00127-HEV1 and GW5074) and that enviroxime-like compounds may have targets other than PI kinases for their antiviral effect.
Figures


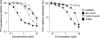
References
-
- Arita, M., N. Nagata, T. Sata, T. Miyamura, and H. Shimizu. 2006. Quantitative analysis of poliomyelitis-like paralysis in mice induced by a poliovirus replicon. J. Gen. Virol. 87:3317-3327. - PubMed
-
- Arita, M., Y. Takebe, T. Wakita, and H. Shimizu. 2010. A bifunctional anti-enterovirus compound that inhibits replication and early stage of enterovirus 71 infection. J. Gen. Virol. 91:2734-2744. - PubMed
-
- Arita, M., T. Wakita, and H. Shimizu. 2009. Cellular kinase inhibitors that suppress enterovirus replication have a conserved target in viral protein 3A similar to that of enviroxime. J. Gen. Virol. 90:1869-1879. - PubMed
-
- Arita, M., T. Wakita, and H. Shimizu. 2008. Characterization of pharmacologically active compounds that inhibit poliovirus and enterovirus 71 infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 89:2518-2530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

