The herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript can protect neuron-derived C1300 and Neuro2A cells from granzyme B-induced apoptosis and CD8 T-cell killing
- PMID: 21177822
- PMCID: PMC3067767
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01791-10
The herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript can protect neuron-derived C1300 and Neuro2A cells from granzyme B-induced apoptosis and CD8 T-cell killing
Abstract
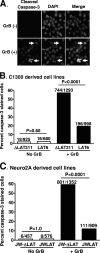
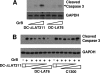
The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) latency-associated transcript (LAT) is the only HSV-1 gene transcript abundantly expressed throughout latency. LAT null mutants have a significantly reduced reactivation phenotype. LAT's antiapoptosis activity is the major LAT factor involved in supporting the wild-type reactivation phenotype. During HSV-1 latency, some ganglionic neurons are surrounded by CD8 T cells, and it has been proposed that these CD8 T cells help maintain HSV-1 latency by suppressing viral reactivations. Surprisingly, despite injection of cytotoxic lytic granules by these CD8 T cells into latently infected neurons, neither apoptosis nor neuronal cell death appears to occur. We hypothesized that protection of latently infected neurons against cytotoxic CD8 T-cell killing is due to LAT's antiapoptosis activity. Since CD8 T-cell cytotoxic lytic granule-mediated apoptosis is critically dependent on granzyme B (GrB), we examined LAT's ability to block GrB-induced apoptosis. We report here that (i) LAT can interfere with GrB-induced apoptosis in cell cultures, (ii) LAT can block GrB-induced cleavage (activation) of caspase-3 both in cell culture and in a cell-free in vitro cell extract assay, and (iii) LAT can protect C1300 and Neuro2A cells from cytotoxic CD8 T-cell killing in vitro. These findings support the hypothesis that LAT's antiapoptosis activity can protect latently infected neurons from being killed by CD8 T-cell lytic granules in vivo.
Figures




References
-
- Adrain, C., B. M. Murphy, and S. J. Martin. 2005. Molecular ordering of the caspase activation cascade initiated by the cytotoxic T lymphocyte/natural killer (CTL/NK) protease granzyme B. J. Biol. Chem. 280:4663-4673. - PubMed
-
- Aubert, M., and J. A. Blaho. 2001. Modulation of apoptosis during herpes simplex virus infection in human cells. Microbes Infect. 3:859-866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS33768/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY019896/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS033768/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EY014900/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014900/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P20RR15635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EY013191/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013191/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY019896/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018171/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY018171/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS033768/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

