SPP1 genotype is a determinant of disease severity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 21178099
- PMCID: PMC3034396
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318207afeb
SPP1 genotype is a determinant of disease severity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Objective: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common single-gene lethal disorder. Substantial patient-patient variability in disease onset and progression and response to glucocorticoids is seen, suggesting genetic or environmental modifiers.
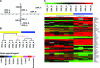
Methods: Two DMD cohorts were used as test and validation groups to define genetic modifiers: a Padova longitudinal cohort (n = 106) and the Cooperative International Neuromuscular Research Group (CINRG) cross-sectional natural history cohort (n = 156). Single nucleotide polymorphisms to be genotyped were selected from mRNA profiling in patients with severe vs mild DMD, and genome-wide association studies in metabolism and polymorphisms influencing muscle phenotypes in normal volunteers were studied.
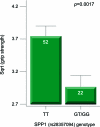
Results: Effects on both disease progression and response to glucocorticoids were observed with polymorphism rs28357094 in the gene promoter of SPP1 (osteopontin). The G allele (dominant model; 35% of subjects) was associated with more rapid progression (Padova cohort log rank p = 0.003), and 12%-19% less grip strength (CINRG cohort p = 0.0003).
Conclusions: Osteopontin genotype is a genetic modifier of disease severity in Duchenne dystrophy. Inclusion of genotype data as a covariate or in inclusion criteria in DMD clinical trials would reduce intersubject variance, and increase sensitivity of the trials, particularly in older subjects.
Figures

Comment in
-
Predicting the severity of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implications for treatment.Neurology. 2011 Jan 18;76(3):208-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182074c0e. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21178098 No abstract available.
-
SPP1 genotype is a determinant of disease severity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: predicting the severity of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: implications for treatment.Neurology. 2011 Nov 15;77(20):1858; author reply 1858-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318239b9ae. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 22084278 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 1987; 51: 919–928 - PubMed
-
- Bushby K, Muntoni F, Urtizberea A, et al. Report on the 124th ENMC International Workshop: treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: defining the gold standards of management in the use of corticosteroids. Neuromuscul Disord 2004; 14: 526–534 - PubMed
-
- Moxley RT, Ashwal S, Pandya S, et al. Practice parameter: corticosteroid treatment of Duchenne dystrophy. Neurology 2005; 64: 13–20 - PubMed
-
- Mayhew JE, Florence JM, Mayhew TP, et al. Reliable surrogate outcome measures in multicenter clinical trials of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2007; 35: 36–42 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
