Epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation
- PMID: 21178119
- PMCID: PMC3144097
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034510378683
Epigenetic mechanisms in inflammation
Abstract
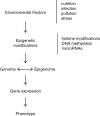
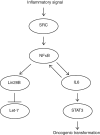
Epigenetic modifications occur in response to environmental changes and play a fundamental role in gene expression following environmental stimuli. Major epigenetic events include methylation and acetylation of histones and regulatory factors, DNA methylation, and small non-coding RNAs. Diet, pollution, infections, and other environmental factors have profound effects on epigenetic modifications and trigger susceptibility to diseases. Despite a growing body of literature addressing the role of the environment on gene expression, very little is known about the epigenetic pathways involved in the modulation of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory genes. This review summarizes the current knowledge about epigenetic control mechanisms during the inflammatory response.
Figures

References
-
- Adcock IM, Tsaprouni L, Bhavsar P, Ito K. (2007). Epigenetic regulation of airway inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol 19:694-700 - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS. (2003). A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423:659-663 - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. (2009). Targeting the epigenome in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:693-696 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

