Combining genome-wide data from humans and animal models of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 21178769
- PMCID: PMC3347921
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328342a375
Combining genome-wide data from humans and animal models of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis
Abstract
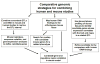
Purpose of review: Comparative genomics allows researchers to combine genome-wide association data from humans with studies in animal models in order to assist in the identification of the genes and the genetic variants that modify susceptibility to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.
Recent findings: Association and linkage studies in human and rodent species have been successful in identifying genetic loci associated with complex traits, but have been less robust in identifying and validating the responsible gene and/or genetic variants. Recent technological advancements have assisted in the development of comparative genomic approaches, which rely on the combination of human and rodent datasets and bioinformatics tools, followed by the narrowing of concordant loci and improved identification of candidate genes and genetic variants. Additionally, candidate genes and genetic variants identified by these methods have been further validated and functionally investigated in animal models, a process that is not feasible in humans.
Summary: Comparative genomic approaches have led to the identification and validation of several new genes, including a few not previously implicated, as modifiers of plasma lipid levels and atherosclerosis, yielding new insights into the biological mechanisms of these complex traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Teslovich TM, Musunuru K, Smith AV, et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature. 2010;466:707–713. GWA study of more than 100,000 individuals of European ancestry that identified 95 common variants associated with human plasma levels of HDL, LDL, TC and TG. This study also validated three candidate genes in animal models demonstrating their role in regulating plasma lipid levels. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frazer KA, Murray SS, Schork NJ, Topol EJ. Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

