Cytokine profiles in asthma families depend on age and phenotype
- PMID: 21179211
- PMCID: PMC3001464
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014299
Cytokine profiles in asthma families depend on age and phenotype
Abstract
Background: Circulating cytokine patterns may be relevant for the diagnosis of asthma, for the discrimination of certain phenotypes, and prognostic factors for exacerbation of disease.
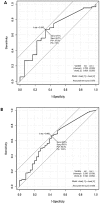
Methodology/principal findings: In this study we investigated serum samples from 944 individuals of 218 asthma-affected families by a multiplex, microsphere based system detecting at high sensitivity eleven asthma associated mediators: eotaxin (CCL11), granulocyte macrophage stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interferon gamma (IFNγ), interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12 (p40), IL-13, IL-17 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα). Single cytokine levels were largely similar between asthmatic and healthy individuals when analysing asthma as single disease entity. Regulatory differences between parental and pediatric asthma were reflected by six of the eleven mediators analyzed (eotaxin, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, TNFα). IL-12 (p40) and IL-5 were the best predictor for extrinsic asthma in children with an increased odds ratio of 2.85 and 1.96 per log pg/ml increase (IL-12 (p40): 1.2-6.8, p=0.019, and IL-5: 1.2-2.5, p=0.025). Frequent asthma attacks in children are associated with elevated IL-5 serum levels (p=0.013). Cytokine patterns seem to be individually balanced in both, healthy and diseased adults and children, with various cytokines correlating among each other (IL-17 and IFNγ (rs=0.67), IL-4 and IL-5 (rs=0.55), IFNγ and GM-CSF (rs=0.54)).
Conclusion/significance: Our data support mainly an age- but also an asthma phenotype-dependent systemic immune regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Anderson GP. Endotyping asthma: new insights into key pathogenic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous disease. Lancet. 2008;372:1107–1119. - PubMed
-
- Larche M, Robinson DS, Kay AB. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:450–463; quiz 464. - PubMed
-
- Robinson DS, Hamid Q, Ying S, Tsicopoulos A, Barkans J, et al. Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Cooper AM, Khader SA. IL-12p40: an inherently agonistic cytokine. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

