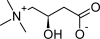
Protective effect of L-carnitine and coenzyme Q10 on CCl₄-induced liver injury in rats
- PMID: 21179323
- PMCID: PMC3007612
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1006-02
Protective effect of L-carnitine and coenzyme Q10 on CCl₄-induced liver injury in rats
Abstract
This study provides an information about the mechanisms of liver injury induced by CCl(4), and determines the influence of administration of L-carnitine or/and CoQ10 as prophylactic agents against CCl(4) deteriorative effect. The study was carried out on 80 adult male albino rats divided into eight groups, 10 animals each, as follows: four normal groups (control, treated with L-carnitine, treated with CoQ10, and treated with a combination of Lcarnitine and CoQ10) and four liver injury groups treated with CCl(4) (control, treated with L-carnitine, treated with CoQ10, and treated with a combination of L-carnitine and CoQ10). Liver injury was induced by s.c. injection of a single dose of CCl(4) (1 ml/kg). L-carnitine (50 mg/kg/day) was given i.p. for four successive days 24 hours before CCl(4) injection, and CoQ10 (200 mg/kg) was given as a single i.p. dose 24 hours before CCl(4) injection. Animals were sacrificed 24 hours after CCl(4) injection, blood samples were withdrawn and liver tissue samples were homogenized. The levels of the following parameters were determined: hepatic reduced glutathione, serum ALT and AST, hepatic lipid peroxides, hepatic vitamin C, hepatic and serum total protein, serum albumin, serum sialic acid, serum nitrite, and serum and hepatic total LDH activities and LDH isoenzymes. The obtained data revealed that CCl(4) injection produced a significant decrease in reduced glutathione content, vitamin C, total protein and albumin levels. However, there was a significant increase in serum ALT and AST activities, lipid peroxides, sialic acid, nitric oxide, serum and hepatic total LDH activities. On the other hand, groups treated with L-carnitine or/and CoQ10 prior to CCl(4) injection showed an improvement in most parameters when compared with cirrhotic control group. It has been concluded that L-carnitine and coenzyme Q10 have a pronounced prophylactic effect against liver damage induced by halogenated alkanes such as carbon tetrachloride.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride; Coenzyme Q10; L-carnitine; Liver; Rats; Serum.
Figures
References
-
- Gruebele A, Zawaski K, Kaplan D, Novak RF. Cytochrome P4502E1- and cytochrome P4502B1/2B2-catalyzed carbon tetrachloride metabolism: effects on signal transduction as demonstrated by altered immediate-early (c-Fos and c-Jun) gene expression and nuclear AP-1 and NF-kappa B transcription factor levels. Drug Metab Dispos. 1996;24:15–22. PMid:8825185. - PubMed
-
- Bertelli A, Cerrati A, Giovannini L, Mian M, Spaggiari P, Bertelli AA. Protective Action Of L-Carnitine And Coenzyme Q10 Against Hepatic Triglyceride Infiltration Induced By Hyperbaric Oxygen And Ethanol. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1993;2:65–68. PMid:8223144. - PubMed
-
- Walter P, Schaffhauser A. L-Carnitine, A Vitamin-Like Substance For Functional Food. Ann Nutr Metab. 2000;44:75–96. doi:10.1159/000012825. - PubMed
-
- Littarru GP. Energy and Defense. Facts and Perspectives On Coenzyme Q10 In Biology And Medicine. Casa Editrice Scientifica Internazionale. 1994:1–91.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources