Live imaging of innate immune cell sensing of transformed cells in zebrafish larvae: parallels between tumor initiation and wound inflammation
- PMID: 21179501
- PMCID: PMC3001901
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000562
Live imaging of innate immune cell sensing of transformed cells in zebrafish larvae: parallels between tumor initiation and wound inflammation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Live Imaging of Innate Immune Cell Sensing of Transformed Cells in Zebrafish Larvae: Parallels between Tumor Initiation and Wound Inflammation.PLoS Biol. 2016 Feb 11;14(2):e1002377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002377. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 26866370 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
It has not previously been possible to live image the earliest interactions between the host environment and oncogene-transformed cells as they initiate formation of cancers within an organism. Here we take advantage of the translucency of zebrafish larvae to observe the host innate immune cell response as oncogene-transformed melanoblasts and goblet cells multiply within the larval skin. Our studies indicate activation of leukocytes at very early stages in larvae carrying a transformed cell burden. Locally, we see recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages by 48 h post-fertilization, when transformed cells are still only singletons or doublets, and soon after this we see intimate associations between immune and transformed cells and frequent examples of cytoplasmic tethers linking the two cell types, as well as engulfment of transformed cells by both neutrophils and macrophages. We show that a major component of the signal drawing inflammatory cells to oncogenic HRAS(G12V)-transformed cells is H(2)O(2), which is also a key damage cue responsible for recruiting neutrophils to a wound. Our short-term blocking experiments show that preventing recruitment of immune cells at these early stages results in reduced growth of transformed cell clones and suggests that immune cells may provide a source of trophic support to the transformed cells just as they do at a site of tissue repair. These parallels between the inflammatory responses to transformed cells and to wounds reinforce the suggestion by others that cancers resemble non-healing wounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
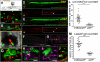





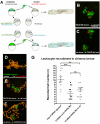

Comment in
-
Cancer courts immune response to aid growth.PLoS Biol. 2010 Dec 14;8(12):e1001004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001004. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 21179500 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler K. W. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg R. A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1073–1081. - PubMed
-
- Allavena P, Garlanda C, Borrello M. G, Sica A, Mantovani A. Pathways connecting inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

