Distinct functions for the Drosophila piRNA pathway in genome maintenance and telomere protection
- PMID: 21179579
- PMCID: PMC3003142
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001246
Distinct functions for the Drosophila piRNA pathway in genome maintenance and telomere protection
Abstract
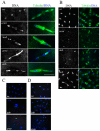
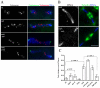
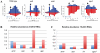
Transposons and other selfish DNA elements can be found in all phyla, and mobilization of these elements can compromise genome integrity. The piRNA (PIWI-interacting RNA) pathway silences transposons in the germline, but it is unclear if this pathway has additional functions during development. Here we show that mutations in the Drosophila piRNA pathway genes, armi, aub, ago3, and rhi, lead to extensive fragmentation of the zygotic genome during the cleavage stage of embryonic divisions. Additionally, aub and armi show defects in telomere resolution during meiosis and the cleavage divisions; and mutations in lig-IV, which disrupt non-homologous end joining, suppress these fusions. By contrast, lig-IV mutations enhance chromosome fragmentation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation studies show that aub and armi mutations disrupt telomere binding of HOAP, which is a component of the telomere protection complex, and reduce expression of a subpopulation of 19- to 22-nt telomere-specific piRNAs. Mutations in rhi and ago3, by contrast, do not block HOAP binding or production of these piRNAs. These findings uncover genetically separable functions for the Drosophila piRNA pathway. The aub, armi, rhi, and ago3 genes silence transposons and maintain chromosome integrity during cleavage-stage embryonic divisions. However, the aub and armi genes have an additional function in assembly of the telomere protection complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Klattenhoff C, Bratu DP, McGinnis-Schultz N, Koppetsch BS, Cook HA, et al. Drosophila rasiRNA pathway mutations disrupt embryonic axis specification through activation of an ATR/Chk2 DNA damage response. Developmental cell. 2007;12:45–55. - PubMed
-
- Cook H, Koppetsch B, Wu J, Theurkauf W. The Drosophila SDE3 Homolog armitage Is Required for oskar mRNA Silencing and Embryonic Axis Specification. Cell. 2004;116:817–829. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Naumova NM, Tulin AV, Vagin VV, Rozovsky YM, et al. Double-stranded RNA-mediated silencing of genomic tandem repeats and transposable elements in the D. melanogaster germline. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1017–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

