Variable Selection for Qualitative Interactions
- PMID: 21179592
- PMCID: PMC3003934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stamet.2009.05.003
Variable Selection for Qualitative Interactions
Abstract
In this article we discuss variable selection for decision making with focus on decisions regarding when to provide treatment and which treatment to provide. Current variable selection techniques were developed for use in a supervised learning setting where the goal is prediction of the response. These techniques often downplay the importance of interaction variables that have small predictive ability but that are critical when the ultimate goal is decision making rather than prediction. We propose two new techniques designed specifically to find variables that aid in decision making. Simulation results are given along with an application of the methods on data from a randomized controlled trial for the treatment of depression.
Figures
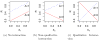
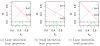


References
-
- Assmann SF, Pocock SJ, Enos LE, Kasten LE. Subgroup analysis and other (mis)uses of baseline data in clinical trials. The Lancet. 2000;355:1064–1069. - PubMed
-
- Beta-Blocker Pooling Project Research Group. The beta-blocker pooling project (bbpp): Subgroup findings from randomized trials in post infarction patients. The Eropean Heart Journal. 1988;9:8–16. - PubMed
-
- Byar DP, Corle DK. Selecting optimal treatment in clinical trials using covariate information. Journal of Chronic Diseases. 1977;30:445–459. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2. Lawrence Earlbaum Associates; Hillsdale, NJ: 1988.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
