Strand-specific real-time RT-PCR for distinguishing influenza vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA
- PMID: 21185869
- PMCID: PMC3049850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.12.014
Strand-specific real-time RT-PCR for distinguishing influenza vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA
Abstract
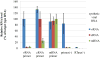
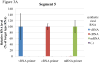
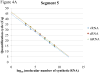
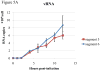
Real-time RT-PCR is used to quantify individual influenza viral RNAs. However, conventional real-time RT-PCR, using strand-specific primers, has been shown to produce not only the anticipated strand-specific products, but also substantial amounts of non-strand-specific products, indicating lack of specificity. Therefore, in this study, a novel strand-specific real-time RT-PCR method was established to quantify the three types of influenza viral RNA (vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA) separately. This method is based on reverse transcription using tagged primers to add a 'tag' sequence at the 5' end and the hot-start method. Real-time PCR using the 'tag' portion as the forward primer and a segment-specific reverse primer ensured the specificity for quantifying the three types of RNA. Using this method, specific target RNA was detected at 100-100,000-folds higher level than other types of RNA. This method was also used to evaluate the vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA levels of segments 5 and 6 in MDCK cells infected with influenza A virus at different time point post-infections. The cRNA level was 1/10 to 1/100 lower than that of the vRNA and mRNA. Moreover, different dynamics of vRNA, cRNA, and mRNA synthesis were observed; the copy number of the vRNA gradually increased throughout the infection, the cRNA increased and then plateaued, while the mRNA increased and then decreased. This novel method thus provides data critical for understanding the influenza virus life cycle, including transcription, replication, and genome incorporation into virions.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
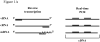
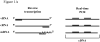




References
-
- Craggs J, Ball J, Thomson B, Irving W, Grabowska A. Development of a strand-specific RT-PCR based assay to detect the replicative form of hepatitis C virus RNA. J Virol Methods. 2001;94:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Hatada E, Hasegawa M, Mukaigawa J, Shimizu K, Fukuda R. Control of influenza virus gene expression: quantitative analysis of each viral RNA species in infected cells. J Biochem. 1989;105:537–546. - PubMed
-
- Karlas A, Machuy N, Shin Y, Pleissner K, Artarini A, Heuer D, Becker D, Khalil H, Ogilvie L, Hess S, Mäurer A, Müller E, Wolff T, Rudel T, Meyer T. Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies human host factors crucial for influenza virus replication. Nature. 2010;463:818–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

