Early-childhood neurodevelopmental outcomes are not improving for infants born at <25 weeks' gestational age
- PMID: 21187312
- PMCID: PMC3375467
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-1150
Early-childhood neurodevelopmental outcomes are not improving for infants born at <25 weeks' gestational age
Abstract
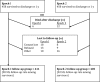
Objective: We compared neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 to 22 months' corrected age of infants born with extremely low birth weight at an estimated gestational age of <25 weeks during 2 periods: 1999-2001 (epoch 1) and 2002-2004 (epoch 2).
Patients and methods: We conducted a multicenter, retrospective analysis of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Perinatal and neonatal variables and outcomes were compared between epochs. Neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 to 22 months' corrected age were evaluated with neurologic exams and Bayley Scales of Infant Development II. Logistic regression analyses determined the independent risk of epoch for adverse outcomes.
Results: Infant survival was similar between epochs (epoch 1, 35.4%, vs epoch 2, 32.3%; P = .09). A total of 411 of 452 surviving infants in epoch 1 and 405 of 438 surviving infants in epoch 2 were evaluated at 18 to 22 months' corrected age. Cesarean delivery (P = .03), surgery for patent ductus arteriosus (P = .004), and late sepsis (P = .01) were more common in epoch 2, but postnatal steroid use was dramatically reduced (63.5% vs 32.8%; P < .0001). Adverse outcomes at 18 to 22 months' corrected age were common in both epochs. Moderate-to-severe cerebral palsy was diagnosed in 11.1% of surviving infants in epoch 1 and 14.9% in epoch 2 (adjusted odds ratio [OR]: 1.52 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.86-2.71]; P = .15), the Mental Developmental Index was <70 in 44.9% in epoch 1 and 51% in epoch 2 (OR: 1.30 [95% CI: 0.91-1.87]; P = .15), and neurodevelopmental impairment was diagnosed in 50.1% of surviving infants in epoch 1 and 58.7% in epoch 2 (OR: 1.4 [95% CI: 0.98-2.04]; P = .07).
Conclusions: Early-childhood outcomes for infants born at <25 weeks' estimated gestational age were unchanged between the 2 periods.
Figures
References
-
- Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196(2):147.e1–147.e8 - PubMed
-
- Hakansson S, Farooqui A, Homgren PA, Serenius F, Hogberg U. Proactive management promotes outcome in extremely preterm infants: a population-based comparison of two perinatal management strategies. Pediatrics. 2004;114(1):58–64 - PubMed
-
- Serenius F, Ewald U, Farooqui A, Holmgren PA, Hakansson S, Sedin G. Short-term outcome after active perinatal management at 23–25 weeks of gestation: a study from two Swedish tertiary care centres. Part 2: infant survival. Acta Paediatr. 2004;93(8):1081–1089 - PubMed
-
- Doyle LW; Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group Neonatal intensive care at borderline viability: is it worth it? Early Hum Dev. 2004;80(2):103–113 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR6022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical