Tuning the ion selectivity of tetrameric cation channels by changing the number of ion binding sites
- PMID: 21187421
- PMCID: PMC3021048
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1013636108
Tuning the ion selectivity of tetrameric cation channels by changing the number of ion binding sites
Abstract
Selective ion conduction across ion channel pores is central to cellular physiology. To understand the underlying principles of ion selectivity in tetrameric cation channels, we engineered a set of cation channel pores based on the nonselective NaK channel and determined their structures to high resolution. These structures showcase an ensemble of selectivity filters with a various number of contiguous ion binding sites ranging from 2 to 4, with each individual site maintaining a geometry and ligand environment virtually identical to that of equivalent sites in K(+) channel selectivity filters. Combined with single channel electrophysiology, we show that only the channel with four ion binding sites is K(+) selective, whereas those with two or three are nonselective and permeate Na(+) and K(+) equally well. These observations strongly suggest that the number of contiguous ion binding sites in a single file is the key determinant of the channel's selectivity properties and the presence of four sites in K(+) channels is essential for highly selective and efficient permeation of K(+) ions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
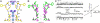
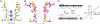
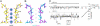
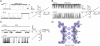
Comment in
-
Mechanism of K+/Na+ selectivity in potassium channels from the perspective of the non-selective bacterial channel NaK.Channels (Austin). 2011 May-Jun;5(3):198-200. doi: 10.4161/chan.5.3.15873. Epub 2011 May 1. Channels (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21540644
References
-
- Doyle DA, et al. The structure of the potassium channel: Molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1998;280:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Morais-Cabral JH, Kaufman A, MacKinnon R. Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 A resolution. Nature. 2001;414:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Valiyaveetil FI, Leonetti M, Muir TW, Mackinnon R. Ion selectivity in a semisynthetic K+ channel locked in the conductive conformation. Science. 2006;314:1004–1007. - PubMed
-
- Long SB, Tao X, Campbell EB, MacKinnon R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature. 2007;450:376–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

