PI-103 and sorafenib inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways
- PMID: 21187475
- PMCID: PMC3141822
PI-103 and sorafenib inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways
Abstract
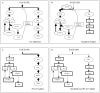
Background: Aberrant Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways are found in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study reports how sorafenib (a multi-kinase inhibitor) and PI-103 (a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor) alone and in combination inhibit the proliferation of the HCC cell line, Huh7.
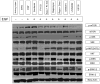
Materials and methods: Huh7 proliferation was assayed by 3H-thymidine incorporation and by MTT assay. Western blot was used to detect phosphorylation of the key enzymes in the Ras/Raf and PI3K pathways.
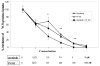
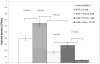
Results: Sorafenib and PI-103, as single agents inhibited Huh7 proliferation and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated Huh7 proliferation in a dose-dependent fashion; the combination of sorafenib and PI-103 produced synergistic effects. EGF increased phosphorylation of MEK and ERK, key Ras/Raf downstream signaling proteins; this activation was inhibited by sorafenib. However, sorafenib as a single agent increased AKT(Ser473) and mTOR phosphorylation. EGF-stimulated activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway components was inhibited by PI-103. PI-103 is a potent inhibitor of AKT(Ser473) phosphorylation; in contrast, rapamycin stimulated AKT(Ser473) phosphorylation. It was found that PI-103, as a single agent, stimulated MEK and ERK phosphorylation. However, the combination of sorafenib and PI-103 caused inhibition of all the tested kinases in the Ras/Raf and PI3K pathways.
Conclusion: The combination of sorafenib and PI-103 can significantly inhibit EGF-stimulated Huh7 proliferation by blocking both Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Befeler AS, Hayashi PH, Di Bisceglie AM. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1752–1764. - PubMed
-
- Strumberg D. Preclinical and clinical development of the oral multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in cancer treatment. Drugs Today (Barc ) 2005;41:773–784. - PubMed
-
- Minguez B, Tovar V, Chiang D, Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and molecular therapies. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009;25:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Chaparro M, Gonzalez ML, Trapero-Marugan M, Medina J, Moreno-Otero R. Review article: pharmacological therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib and other oral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:1269–1277. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
