Comparative study of proton pump inhibitors on dexamethasone plus pylorus ligation induced ulcer model in rats
- PMID: 21188049
- PMCID: PMC3003173
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.70486
Comparative study of proton pump inhibitors on dexamethasone plus pylorus ligation induced ulcer model in rats
Abstract
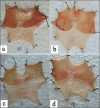
The present study was designed to compare ulcer protective effect of proton pump inhibitors viz. omeprazole, rabeprazole and lansoprazole against dexamethasone plus pylorus ligation induced ulcer model. Dexamethasone (5 mg/kg) was used as an ulcerogen. Dexamethasone suspended in 1% CMC in water was given orally to all the rats 15 min after the pylorus ligation. Omeprazole (20 mg/kg), rabeprazole (20 mg/kg), and lansoprazole (20 mg/kg) were administered by oral route 30 min prior to ligation was used for ulcer protective studies, gastric secretion and mucosal studies. Effects of proton pump inhibitors were determined by the evaluation of various biochemical parameters such as ulcer index, free and total acidity, gastric pH, mucin, pepsin and total proteins. Oral administration of proton pump inhibitors showed significant reduction in gastric acid secretion and ulcer protective activity against dexamethasone plus pylorus ligation induced ulcer model. The % protection of omeprazole, rabeprazole and lansoprazole was 84.04, 89.36 and 79.78, respectively. Rabeprazole significantly inhibited the acid-pepsin secretion and increased the gastric mucin secretion. The observations made in the present study suggest that rabeprazole is the most effective gastric antisecretory and ulcer healing agent as compared to omeprazole and lansoprazole.
Keywords: Dexamethasone; PPIs; mucosal offensive and defense factors.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman JD, Haile PM, Siegelaaub AB, Seltzer CE. Cigarette, alcohol, coffee and peptic ulcer. N Engl J Med. 1974;290:469–73. - PubMed
-
- Manjari V, Das UN. Oxidant stress, anti-oxidants, nitric acid and essential fatty acids in peptic ulcer disease. Prostaglandins, Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1998;59:401–6. - PubMed
-
- Megraud F, Lamouliatte H. Helicobacter pylori and duodenal ulcer evidence suggesting causation. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;5:769–72. - PubMed
-
- Dujovne CA, Azarnoff DL. Clinical complications of corticosteroid therapy. Med Clin North Am. 1973;57:1331–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources