Optimal management of cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome
- PMID: 21188094
- PMCID: PMC3004581
- DOI: 10.2147/cmar.s7101
Optimal management of cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome
Abstract
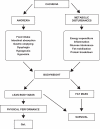
According to a recent consensus, cachexia is a complex metabolic syndrome associated with underlying illness and characterized by loss of muscle with or without loss of fat mass. The prominent clinical feature of cachexia is weight loss. Cachexia occurs in the majority of cancer patients before death and it is responsible for the deaths of 22% of cancer patients. Although bodyweight is the most important endpoint of any cachexia treatment, body composition, physical performance and quality of life should be monitored. From the results presented here, one can speculate that a single therapy may not be completely successful in the treatment of cachexia. From this point of view, treatments involving different combinations are more likely to be successful. The objectives of any therapeutic combination are two-fold: an anticatabolic aim directed towards both fat and muscle catabolism and an anabolic objective leading to the synthesis of macromolecules such as contractile proteins.
Keywords: anorexia; cancer; drugs; nutraceuticals; wasting.
Figures

References
-
- Evans WJ, Morley JE, Argilés J, et al. Cachexia: a new definition. Clin Nutr. 2008;27(6):793–799. - PubMed
-
- Warren S. The immediate cause of death in cancer. Am J Med Sci. 1932;184:610–613.
-
- Mulligan K, Schambelan M. Anabolic treatment with GH, IGF-I, or anabolic steroids in patients with HIV-associated wasting. Int J Cardiol. 2002;85(1):151–159. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Sharma R. The syndrome of cardiac cachexia. Int J Cardiol. 2002;85(1):51–66. - PubMed
-
- Argilés JM, Álvarez B, López-Soriano FJ. The metabolic basis of cancer cachexia. Med Res Rev. 1997;17(5):477–498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

