In vivo activation of ROCK1 by insulin is impaired in skeletal muscle of humans with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 21189360
- PMCID: PMC3064006
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00538.2010
In vivo activation of ROCK1 by insulin is impaired in skeletal muscle of humans with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
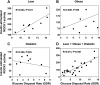
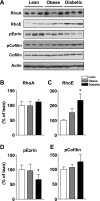
To determine whether serine/threonine ROCK1 is activated by insulin in vivo in humans and whether impaired activation of ROCK1 could play a role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance, we measured the activity of ROCK1 and the protein content of the Rho family in vastus lateralis muscle of lean, obese nondiabetic, and obese type 2 diabetic subjects. Biopsies were taken after an overnight fast and after a 3-h hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp. Insulin-stimulated GDR was reduced 38% in obese nondiabetic subjects compared with lean, 62% in obese diabetic subjects compared with lean, and 39% in obese diabetic compared with obese nondiabetic subjects (all comparisons P < 0.001). Insulin-stimulated IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation is impaired 41-48% in diabetic subjects compared with lean or obese subjects. Basal activity of ROCK1 was similar in all groups. Insulin increased ROCK1 activity 2.1-fold in lean and 1.7-fold in obese nondiabetic subjects in muscle. However, ROCK1 activity did not increase in response to insulin in muscle of obese type 2 diabetic subjects without change in ROCK1 protein levels. Importantly, insulin-stimulated ROCK1 activity was positively correlated with insulin-mediated GDR in lean subjects (P < 0.01) but not in obese or type 2 diabetic subjects. Moreover, RhoE GTPase that inhibits the catalytic activity of ROCK1 by binding to the kinase domain of the enzyme is notably increased in obese type 2 diabetic subjects, accounting for defective ROCK1 activity. Thus, these data suggest that ROCK1 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of resistance to insulin action on glucose disposal in muscle of obese type 2 diabetic subjects.
Figures
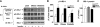
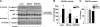
References
-
- No authors listed Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 21, Suppl 1: S5–S22, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J Biol Chem 277: 1531–1537, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Fukata Y, Kaibuchi K. Regulation and functions of Rho-associated kinase. Exp Cell Res 261: 44–51, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Begum N, Sandu OA, Ito M, Lohmann SM, Smolenski A. Active Rho kinase (ROK-alpha) associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and inhibits insulin signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 277: 6214–6222, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Björnholm M, Kawano Y, Lehtihet M, Zierath JR. Insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in skeletal muscle from NIDDM subjects after in vivo insulin stimulation. Diabetes 46: 524–527, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

