Angiotensin AT₂ receptor stimulation inhibits early renal inflammation in renovascular hypertension
- PMID: 21189405
- PMCID: PMC3060557
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.164202
Angiotensin AT₂ receptor stimulation inhibits early renal inflammation in renovascular hypertension
Abstract
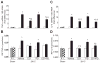
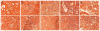
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT₂R) counteracts most effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT(1)R). We hypothesized that direct AT₂R stimulation reduces renal production of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and enhances the production of nitric oxide (NO) and cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cGMP) in the clipped kidney of 2-kidney, 1-clip (2K1C) hypertension rat model. We used Sprague-Dawley rats to evaluate changes in renal interstitial fluid recovery levels of TNF-α, IL-6, NO, and cGMP; renal expression of AT₁R, AT₂R, TGF-β1, TNF-α, and IL-6 in sham and 2K1C rats treated for 4 days with vehicle, AT₂R agonist compound 21 (C21), or AT₂R antagonist PD123319 (PD), alone and combined (n=6, each group). Systolic blood pressure increased significantly in 2K1C and was not influenced by any treatment. Clipped kidneys showed significant increases in renal expression of AT₁R, AT₂R, TNF-α, IL-6, TGF-β1 and decreases in NO and cGMP levels. These factors were not influenced by PD treatment. In contrast, C21 caused significant decrease in renal TNF-α, IL-6, TGF-β1 and an increase in NO and cGMP levels. Combined C21 and PD treatment partially reversed the observed C21 effects. Compared to sham, there were no significant changes in TNF-α, IL-6, TGF-β1, NO, or cGMP in the nonclipped kidneys of 2K1C animals. We conclude that direct AT₂R stimulation reduces early renal inflammatory responses and improves production of NO and cGMP in renovascular hypertension independent of blood pressure reduction.
Figures
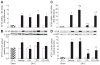


References
-
- Morrissey JJ, Klahr S. Effect of AT2 receptor blockade on the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1999;276:F39–F45. - PubMed
-
- Ozono R, Wang ZQ, Moore AF, Inagami T, Siragy HM, Carey RM. Expression of the subtype 2 angiotensin (AT2) receptor protein in rat kidney. Hypertension. 1997;30:1238–1246. - PubMed
-
- Miyata N, Park F, Li XF, Cowley AW., Jr Distribution of angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1999;277:F437–F446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

