Ruta graveolens L. toxicity in Vampirolepis nana infected mice
- PMID: 21189902
- PMCID: PMC2991689
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.71898
Ruta graveolens L. toxicity in Vampirolepis nana infected mice
Abstract
Objective: To determine possible toxic effects of Ruta graveolens hydroalcoholic extract in gastrointestinal parasitic infection.
Materials and methods: A total of 100 g plant leaves and seeds were powdered and extracted with 1500 mL alcohol/water and administered by gavage to Swiss albino mice infected with Vampirolepis nana. Anti-parasitic evaluation and toxicity assays were carried out in six groups of ten animals each. Treatments were scheduled with both the leaves and the seeds' extracts at doses of 2.5, 5, and 10 mg per gram body weight. Toxicity was comparatively analyzed to a vehicle control group (n = 10) and to a Praziquantel(®) treated. On the fifth day, all the individuals were killed by euthanasia and parasite scores were correlated, giving rise to a relative percentage of elimination to each treatment. Toxicity was achieved by hematology and by clinical chemistry determinations.
Results: The use of the R. graveolens hydroalcoholic extract to treat V. nana infected mice resulted in a mild-to-moderate hepatoxicity associated to a poor anti-parasitic effect. The major proglottids elimination (E%) was achieved at the lowest crude extract concentration with a mild anti-parasitic efficacy from the highest dose; that did not cause a significant elimination of parasites. A decrease of circulating polymorphonuclear-neutrophils associated with a normochromic-normocytic anemia was detected as the extract dose was augmented. The blood aspartate-aminotransferase and alanine-aminotransferase tended be slightly augmented with 100 mg R. graveolens extract.
Conclusion: R. graveolens is an unsafe natural anti-parasitic medicine as its active constituents may be poorly extracted by the popular crude herb infusion. Although it presented a mild anti-parasitic effect in mice, symptoms of natural-products-induced-liver-disease confirmed that its self-medication should be avoided.
Keywords: Anthelmintic activity; Ruta graveolens; Vampirolepis nana; natural-products-induced-liver-disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

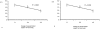
References
-
- Stashenko EE, Acosta R, Martinez JR. High-resolution gas-chromatographic analysis of the secondary metabolites obtained by subcritical-fluid extraction from Colombian rue (Ruta graveolens L.) J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2000;43:379–90. - PubMed
-
- De-Feo V, De-Simone F, Senatore F. Potential allelochemicals from the essential oil of Ruta graveolens. Phytochemistry. 2002;61:573–8. - PubMed
-
- Ivanova A, Mikhova B, Najdenski H, Tsvetkova I, Kostova I. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of Ruta graveolens. Fitoterapia. 2005;76:344–7. - PubMed
-
- Sallal AJ, Alkofahi A. Inhibition of the hemolytic activities of snake and scorpion venoms in Vitro with plant extracts. Biomed Lett. 1996;53:211–5.
-
- El-Agraa SE, El-Badwi SM, Adam SE. Preliminary observations on experimental Ruta graveolens toxicosis in Nubian goats. Trop Anim Health. 2000;34:271–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

