Comparison of analgesic effects of nimesulide, paracetamol, and their combination in animal models
- PMID: 21189904
- PMCID: PMC2991691
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.71913
Comparison of analgesic effects of nimesulide, paracetamol, and their combination in animal models
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the analgesic activity of nimesulide and paracetamol alone and their combination in animal models for the degree of analgesia and the time course of action.
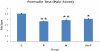
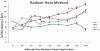
Materials and methods: Analgesia was studied in albino rats using formalin test and in albino mice using writhing test and the radiant heat method. For each test, four groups of six animals each were orally fed with a single dose of nimesulide, paracetamol, and combination of nimesulide + paracetamol and gum acacia as control, respectively.
Results: In all the three test models, all three drug treatments showed significant analgesia (P < 0.001) as compared to control, but there was no significant difference in the analgesia produced by either drugs alone or in combination. The radiant heat method demonstrated a quicker onset and longer duration of action with nimesulide, whereas writhing test showed a quicker onset of action with paracetamol. In formalin test, greater degree of analgesia was seen with individual drugs than that of the combination, though this difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusions: Nimesulide and paracetamol combination offers no advantage over nimesulide alone or paracetamol alone, either in terms of degree of analgesia or onset of action. Therefore, our study supports the reports claiming irrationality of the fixed dose combination of nimesulide and paracetamol.
Keywords: Analgesic effects; nimesulide; paracetamol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of gastric tolerability, antinociceptive and antiinflammatory activity of combination NSAIDs in rats.Indian J Dent Res. 2009 Oct-Dec;20(4):418-22. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.59439. Indian J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 20139563
-
Guaifenesin enhances the analgesic potency of ibuprofen, nimesulide and celecoxib in mice.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009;30(3):352-6. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19855358
-
Evaluation of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of fixed dose combination: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in experimental animals.Indian J Dent Res. 2014 Sep-Oct;25(5):551-4. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.147071. Indian J Dent Res. 2014. PMID: 25511049
-
Nefopam analgesia and its role in multimodal analgesia: A review of preclinical and clinical studies.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Jan;43(1):3-12. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12506. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26475417 Review.
-
Combination analgesia in 2005 - a rational approach: focus on paracetamol-tramadol.Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25 Suppl 1:S16-21. doi: 10.1007/s10067-006-0202-9. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16741784 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of a Versatile UPLC-PDA Method for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Tizanidine, Aceclofenac, and Nimesulide in Their New Combinations.J Anal Methods Chem. 2018 May 14;2018:7463914. doi: 10.1155/2018/7463914. eCollection 2018. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018. PMID: 29888026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burke A, Smyth EM, Fitzgerald GA. Analgesic-antipyretic agents; Pharmacotherapy of gout. In: Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 11th ed. New York: Mcgraw-Hill; 2006. pp. 671–716.
-
- Pharmacological and therapeutic rationale of combination of Nimesulide and paracetamol: Company manuscript. Emcure Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd
-
- Kulkarni SK, Jain NK. Is there any rationale for Nimesulide and paracetamol combination? Indian J Pharmacol. 1999;31:444–5.
-
- Famaey JP. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological evidence of selective cyclooxygenase-2 by nimesulide: An overview. Inflamm Res. 1997;46:437–46. - PubMed
-
- Rabasseda X. Nimesulide: A selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor antiinfammatory drug. Drugs Today. 1996;32:1–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

