Update on pertussis and pertussis immunization
- PMID: 21189928
- PMCID: PMC2994127
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2010.53.5.629
Update on pertussis and pertussis immunization
Abstract
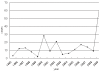
Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory tract disease caused by Bordetella pertussis infection. The clinical manifestation of this infection can be severe enough to cause death. Although pertussis has been supposed to be a vaccine-preventable disease ever since the widespread vaccination of children against pertussis was started, since the 1990s, cases of pertussis and related fatalities are on the rise, especially in countries with high vaccination coverage. In Korea, there have been no deaths due to pertussis since 1990, and the vaccination rate continues to be approximately 94%. However, the number of pertussis cases reported to the Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention has tended to increase in the 2000s, and in 2009, there was an obvious increase in the number of pertussis cases reported. This review aims to present the latest information about the pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pertussis.
Keywords: Outbreak; Pertussis; Vaccination.
Figures

References
-
- Department of Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health Organization. WHO-recommended standards for surveillance of selected vaccinepreventable diseases. Geneva: WHO; 2003. p. 28.
-
- Edwards KM. Overview of pertussis: focus on epidemiology, sources of infection, and long term protection after infant vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24(6 Suppl):S104–S108. - PubMed
-
- Division of Tuberculosis and Bacterial Respiratory Infections: Korea National Health Institute. The report of a survey for pertussis infection status in Korea. Seoul: Korea National Health Institute; 2007. pp. 95–110.
-
- Division of Tuberculosis and Bacterial Respiratory Infections: Korea National Health Institute. Serotypic variations of Bordetella pertussis isolated in Korea. Seoul: Korea National Health Institute; 2008. pp. 621–625.
-
- Division of Tuberculosis and Bacterial Respiratory Infections: Korea National Health Institute. Increasing incidence of pertussis in Korea. Seoul: Korea National Health Institute; 2009. p. 709.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

