Inhibitory effects of curcumin on passive cutaneous anaphylactoid response and compound 48/80-induced mast cell activation
- PMID: 21190003
- PMCID: PMC2998773
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.2010.43.1.36
Inhibitory effects of curcumin on passive cutaneous anaphylactoid response and compound 48/80-induced mast cell activation
Abstract
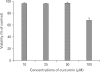
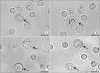
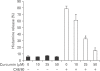
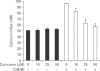
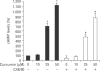
Mast cells participate in allergies and inflammation by secreting a variety of pro-inflammatory mediators. Curcumin, the active component of turmeric, is a polyphenolic phytochemical with anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-allergic properties. The effects of curcumin on compound 48/80-induced mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylactoid reactions are unknown. In this report, we investigated the influences of curcumin on the passive cutaneous anaphylactoid response in vivo and compound 48/80-induced mast cell activation in vitro. The mechanism of action was examined by calcium uptake measurements and cAMP assays in mast cells. Curcumin significantly attenuated the mast cell-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylactoid reaction in an animal model. In agreement with this in vivo activity, curcumin suppressed compound 48/80-induced rat peritoneal mast cell (RPMC) degranulation and histamine release from RPMCs. Moreover, compound 48/80-elicited calcium uptake into RPMCs was reduced in a dose-dependent manner by curcumin. Furthermore, curcumin increased the level of intracellular cAMP and significantly inhibited the compound 48/80-induced reduction of cAMP in RPMCs. These results corroborate the finding that curcumin may have anti-allergic activity.
Keywords: Anaphylactoid reaction; Calcium; Curcumin; Histamine; Mast cell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of atractylone on mast cell-mediated allergic reactions.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Oct 25;258:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.08.015. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27553716
-
Inhibitory effects of epigallocatechin gallate on compound 48/80-induced mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis.Exp Mol Med. 2005 Aug 31;37(4):290-6. doi: 10.1038/emm.2005.39. Exp Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16155406
-
Effects of Anemarrhena asphodeloides on IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis, compound 48/80-induced systemic anaphylaxis and mast cell activation.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013 May;65(4):419-26. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2011.12.006. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 22261360
-
Inhibitory effects of Houttuynia cordata water extracts on anaphylactic reaction and mast cell activation.Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Oct;28(10):1864-8. doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.1864. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005. PMID: 16204936
-
The Na+/K(+)-pump in rat peritoneal mast cells: some aspects of regulation of activity and cellular function.Dan Med Bull. 1995 Nov;42(5):441-54. Dan Med Bull. 1995. PMID: 8747801 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Ingestion Inhibits Mastocytosis and Suppresses Intestinal Anaphylaxis in a Murine Model of Food Allergy.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132467. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132467. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147007 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin inhibits the activation of immunoglobulin e-mediated mast cells and passive systemic anaphylaxis in mice by reducing serum eicosanoid and histamine levels.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014 Jan;22(1):27-34. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2013.092. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014. PMID: 24596618 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin inhibits the pruritus in mice through mast cell MrgprB2 receptor.Inflamm Res. 2023 May;72(5):933-945. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01724-0. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36997814
-
Fish Scale Collagen Peptides Protect against CoCl2/TNF-α-Induced Cytotoxicity and Inflammation via Inhibition of ROS, MAPK, and NF-κB Pathways in HaCaT Cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:9703609. doi: 10.1155/2017/9703609. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28717410 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of NO/cGMP inhibitors in a rat model of anaphylactoid shock.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020 Mar 2;53(3):e8853. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198853. eCollection 2020. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32130289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akagi M, Katakuse Y, Fukuishi N, Kan T, Akagi R. Superoxide anion-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 1994;17:732–734. - PubMed
-
- Allansmith MR, Baird RS, Ross RN, Barney NP, Bloch KJ. Ocular anaphylaxis induced in the rat by topical application of compound 48/80. Dose response and time course study. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1989;192:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Choi YH, Yan GH, Chai OH, et al. Inhibition of anaphylaxis-like reaction and mast cell activation by water extract from the fruiting body of Phellinus linteus. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006a;29:1360–1365. - PubMed
-
- Choi YH, Yan GH, Chai OH, et al. Inhibitory effects of Agaricus blazei on mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis-like reactions. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006b;29:1366–1371. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
