Clinical practice: surgical approaches to urolithiasis in children
- PMID: 21190040
- PMCID: PMC4011548
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-010-1373-6
Clinical practice: surgical approaches to urolithiasis in children
Abstract
The incidence of urolithiasis in children is increasing. Adequate knowledge of treatment modalities and surgical options is therefore essential for every pediatrician. Surgical approaches to urolithiasis in children continue to evolve with advancements in technology and sophistication of current equipment and techniques. Perhaps the most significant development in new techniques is the advent of robotic-assisted laparoscopy. This review, for the general pediatrician, summarizes the most recent pediatric data and guidelines for surgical approaches to treatment of urolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

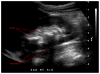
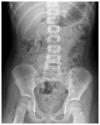

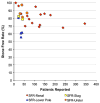



References
-
- Ather MH, Noor MA. Does size and site matter for renal stones up to 30-mm in size in children treated by extracorporeal lithotripsy? Urology. 2003;61(1):212–215. S0090429502021283. discussion 215. - PubMed
-
- Badawy H, Salama A, Eissa M, et al. Percutaneous management of renal calculi: experience with percutaneous nephrolithotomy in 60 children. J Urol. 1999;162(5):1710–1713. S0022-5347(05)68220-1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

