Validation of the World Health Organization tool for situational analysis to assess emergency and essential surgical care at district hospitals in Ghana
- PMID: 21190114
- PMCID: PMC3032911
- DOI: 10.1007/s00268-010-0918-1
Validation of the World Health Organization tool for situational analysis to assess emergency and essential surgical care at district hospitals in Ghana
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization (WHO) Tool for Situational Analysis to Assess Emergency and Essential Surgical Care (hereafter called the WHO Tool) has been used in more than 25 countries and is the largest effort to assess surgical care in the world. However, it has not yet been independently validated. Test-retest reliability is one way to validate the degree to which tests instruments are free from random error. The aim of the present field study was to determine the test-retest reliability of the WHO Tool.
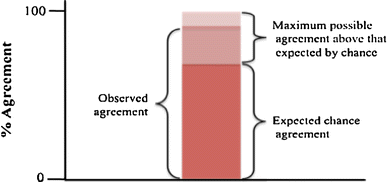
Methods: The WHO Tool was mailed to 10 district hospitals in Ghana. Written instructions were provided along with a letter from the Ghana Health Services requesting the hospital administrator to complete the survey tool. After ensuring delivery and completion of the forms, the study team readministered the WHO Tool at the time of an on-site visit less than 1 month later. The results of the two tests were compared to calculate kappa statistics for each of the 152 questions in the WHO Tool. The kappa statistic is a statistical measure of the degree of agreement above what would be expected based on chance alone.
Results: Ten hospitals were surveyed twice over a short interval (i.e., less than 1 month). Weighted and unweighted kappa statistics were calculated for 152 questions. The median unweighted kappa for the entire survey was 0.43 (interquartile range 0-0.84). The infrastructure section (24 questions) had a median kappa of 0.81; the human resources section (13 questions) had a median kappa of 0.77; the surgical procedures section (67 questions) had a median kappa of 0.00; and the emergency surgical equipment section (48 questions) had a median kappa of 0.81.
Conclusions: Hospital capacity survey questions related to infrastructure characteristics had high reliability. However, questions related to process of care had poor reliability and may benefit from supplemental data gathered by direct observation. Limitations to the study include the small sample size: 10 district hospitals in a single country. Consistent and high correlations calculated from the field testing within the present analysis suggest that the WHO Tool for Situational Analysis is a reliable tool where it measures structure and setting, but it should be revised for measuring process of care.
Figures
References
-
- Debas HT, Gosselin R, McCord C, et al. Surgery. In: Jamison D, et al., editors. Disease control priorities in developing countries. 2. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 1245–1260.
-
- Emergency and Essential Surgical Care (2009) http://www.who.int/surgery/globalinitiative/en/. Accessed 5 April 2010