Heart failure-associated anemia: bone marrow dysfunction and response to erythropoietin
- PMID: 21191566
- PMCID: PMC3056002
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-010-0710-6
Heart failure-associated anemia: bone marrow dysfunction and response to erythropoietin
Abstract
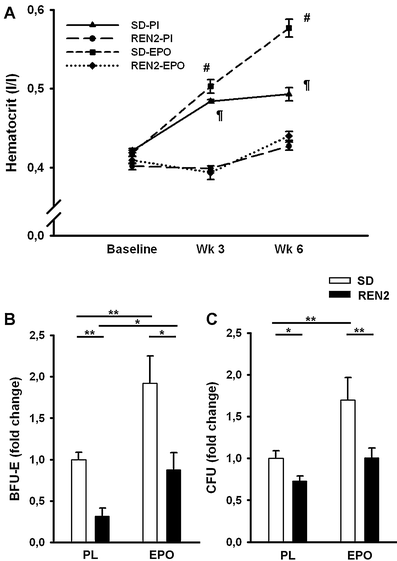
Heart failure (HF)-associated anemia is common and has a poor outcome. Because bone marrow (BM) dysfunction may contribute to HF-associated anemia, we first investigated mechanisms of BM dysfunction in an established model of HF, the transgenic REN2 rat, which is characterized by severe hypertrophy and ventricular dilatation and SD rats as controls. Secondly, we investigated whether stimulation of hematopoiesis with erythropoietin (EPO) could restore anemia and BM dysfunction. After sacrifice, erythropoietic precursors (BFU-E) were isolated from the BM and cultured for 10 days. BFU-E were quantified and transcript abundance of genes involved in erythropoiesis were assayed. Number of BFU-E were severely decreased in BM of REN2 rats compared to SD rats (50 ± 6.2 vs. 6.4 ± 1.7, p < 0.01). EPO treatment increased hematocrit in the SD-EPO group (after 6 weeks, 49 ± 1 vs. 58 ± 1%, p < 0.01); however, in the mildly anemic REN2 rats, there was no effect (43 ± 1 vs. 44 ± 1%). This was paralleled by a 67% decrease in BFU-E in BM of REN2 rats compared to SD (p < 0.01). EPO significantly improved BFU-E in both SD and REN2 but could not restore this to control levels in the REN2 rats. Expression of several genes involved in differentiation (LMO2), mobilization (SDF-1), and iron incorporation (transferrin receptor) of the BM were differentially expressed in REN2 rats compared to SD rats, and EPO did not normalize this. Altogether, these results suggest that BM dysfunction is an important contributor to HF-associated anemia and that EPO is not an effective agent to treat HF-associated anemia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Daily propranolol administration reduces persistent injury-associated anemia after severe trauma and chronic stress.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Apr;82(4):714-721. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001374. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017. PMID: 28099381 Free PMC article.
-
The hypoxia inducible factor/erythropoietin (EPO)/EPO receptor pathway is disturbed in a rat model of chronic kidney disease related anemia.PLoS One. 2018 May 8;13(5):e0196684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196684. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29738538 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal erythroid cell production during erythropoietin treatment of mice occurs by exploiting the splenic microenvironment.Exp Hematol. 1993 Apr;21(4):496-501. Exp Hematol. 1993. PMID: 8462658
-
Mechanisms and treatment of anemia in chronic heart failure.Congest Heart Fail. 2004 Sep-Oct;10(5):243-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-5299.2004.03298.x. Congest Heart Fail. 2004. PMID: 15470302 Review.
-
End-stage renal disease following polycythemia vera: in vitro and in vivo response of erythroid progenitors to erythropoietin and effects of sera on normal erythropoiesis.Nephron. 1998;79(2):142-7. doi: 10.1159/000045016. Nephron. 1998. PMID: 9647492 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic restraint stress after injury and shock is associated with persistent anemia despite prolonged elevation in erythropoietin levels.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015 Jul;79(1):91-6; discussion 96-7. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000686. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015. PMID: 26091320 Free PMC article.
-
Dangshen Erling Decoction Ameliorates Myocardial Hypertrophy via Inhibiting Myocardial Inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:725186. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.725186. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046797 Free PMC article.
-
Discordance between estimated and measured changes in plasma volume among patients with acute heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Feb;9(1):66-76. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13739. Epub 2021 Dec 8. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 34881523 Free PMC article.
-
Serum erythropoietin level predicts the prognosis of chronic heart failure with or without anemia.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Nov;6(5):1327-1331. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1307. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 24223667 Free PMC article.
-
AKIP1, a cardiac hypertrophy induced protein that stimulates cardiomyocyte growth via the Akt pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 28;14(11):21378-93. doi: 10.3390/ijms141121378. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24169435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Meara E, Clayton T, McEntegart MB, McMurray JJ, Lang CC, Roger SD, Young JB, Solomon SD, Granger CB, Ostergren J, et al. Clinical correlates and consequences of anemia in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure: results of the Candesartan in Heart Failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity (CHARM) Program. Circulation. 2006;113:986–994. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.582577. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Meer P, Lipsic E, Westenbrink BD, van de Wal RM, Schoemaker RG, Vellenga E, van Veldhuisen DJ, Voors AA, van Gilst WH. Levels of hematopoiesis inhibitor N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline partially explain the occurrence of anemia in heart failure. Circulation. 2005;112:1743–1747. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.549121. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

