Serotonin receptor diversity in the human colon: Expression of serotonin type 3 receptor subunits 5-HT3C, 5-HT3D, and 5-HT3E
- PMID: 21192076
- PMCID: PMC3056486
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22525
Serotonin receptor diversity in the human colon: Expression of serotonin type 3 receptor subunits 5-HT3C, 5-HT3D, and 5-HT3E
Abstract
Since the first description of 5-HT₃ receptors more than 50 years ago, there has been speculation about the molecular basis of their receptor heterogeneity. We have cloned the genes encoding novel 5-HT3 subunits 5-HT3C, 5-HT3D, and 5-HT3E and have shown that these subunits are able to form functional heteromeric receptors when coexpressed with the 5-HT3A subunit. However, whether these subunits are actually expressed in human tissue remained to be confirmed. In the current study, we performed immunocytochemistry to locate the 5-HT3A as well as the 5-HT3C, 5-HT3D, and 5-HT3E subunits within the human colon. Western blot analysis was used to confirm subunit expression, and RT-PCR was employed to detect transcripts encoding 5-HT₃ receptor subunits in microdissected tissue samples. This investigation revealed, for the first time, that 5-HT3C, 5-HT3D, and 5-HT3E subunits are coexpressed with 5-HT3A in cell bodies of myenteric neurons. Furthermore, 5-HT3A and 5-HT3D were found to be expressed in submucosal plexus of the human large intestine. These data provide a strong basis for future studies of the roles that specific 5-HT₃ receptor subtypes play in the function of the enteric and central nervous systems and the contribution that specific 5-HT₃ receptors make to the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
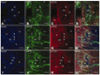
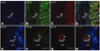

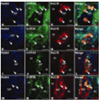


References
-
- Bearcroft CP, Andre EA, Farthing MJ. In vivo effects of the 5-HT3 antagonist alosetron on basal and cholera toxin-induced secretion in the human jejunum: a segmental perfusion study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997;11:1109–1114. - PubMed
-
- Belelli D, Balcarek JM, Hope AG, Peters JA, Lambert JJ, Blackburn TP. Cloning and functional expression of a human 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3AS receptor subunit. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;48:1054–1062. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Kunze WAA, Bornstein JC, Furness JB, Smith ML. Analysis of the responses of myenteric neurons in the small intestine to chemical stimulation of the mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1997;36:G422–G435. - PubMed
-
- Bottner M, Bar F, Von Koschitzky H, Tafazzoli K, Roblick UJ, Bruch HP, Wedel T. Laser microdissection as a new tool to investigate site-specific gene expression in enteric ganglia of the human intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;22:168–172. e152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

