Small molecule inhibitors as countermeasures for botulinum neurotoxin intoxication
- PMID: 21193845
- PMCID: PMC6259422
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16010202
Small molecule inhibitors as countermeasures for botulinum neurotoxin intoxication
Abstract
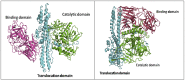
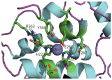
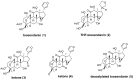
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) are the most potent of known toxins and are listed as category A biothreat agents by the U.S. CDC. The BoNT-mediated proteolysis of SNARE proteins inhibits the exocytosis of acetylcholine into neuromuscular junctions, leading to life-threatening flaccid paralysis. Currently, the only therapy for BoNT intoxication (which results in the disease state botulism) includes experimental preventative antibodies and long-term supportive care. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify and develop inhibitors that will serve as both prophylactic agents and post-exposure 'rescue' therapeutics. This review focuses on recent progress to discover and develop small molecule inhibitors as therapeutic countermeasures for BoNT intoxication.
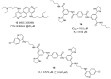
Figures





References
-
- Arnon S.S., Schechter R., Inglesby T.V., Henderson D.A., Bartlett J.G., Ascher M.S., Eitzen E., Fine A.D., Hauer J., Layton M., Lillibridge S., Osterholm M.T., O'Toole T., Parker G., Perl T.M., Russell P.K., Swerdlow D.L., Tonat K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA. 2001;285:1059–1070. - PubMed
-
- Burnett J.C., Schmidt J.J., McGrath C.F., Nguyen T.L., Hermone A.R., Panchal R.G., Vennerstrom J.L., Kodukula K., Zaharevitz D.W., Gussio R., Bavari S. Conformational sampling of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A light chain: Implications for inhibitor binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005;13:333–341. - PubMed
-
- Josko D. Botulin toxin: A weapon in terrorism. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004;17:30–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

