VEGF₁₂₁b and VEGF₁₆₅b are weakly angiogenic isoforms of VEGF-A
- PMID: 21194429
- PMCID: PMC3022671
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-320
VEGF₁₂₁b and VEGF₁₆₅b are weakly angiogenic isoforms of VEGF-A
Abstract
Background: Different isoforms of VEGF-A (mainly VEGF₁₂₁, VEGF₁₆₅ and VEGF189) have been shown to display particular angiogenic properties in the generation of a functional tumor vasculature. Recently, a novel class of VEGF-A isoforms, designated as VEGF(xxx)b, generated through alternative splicing, have been described. Previous studies have suggested that these isoforms may inhibit angiogenesis. In the present work we have produced recombinant VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b proteins in the yeast Pichia pastoris and constructed vectors to overexpress these isoforms and assess their angiogenic potential.
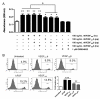
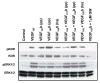
Results: Recombinant VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b proteins generated either in yeasts or mammalian cells activated VEGFR2 and its downstream effector ERK1/2, although to a lesser extent than VEGF₁₆₅. Furthermore, treatment of endothelial cells with VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b increased cell proliferation compared to untreated cells, although such stimulation was lower than that induced by VEGF₁₆₅. Moreover, in vivo angiogenesis assays confirmed angiogenesis stimulation by VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b isoforms. A549 and PC-3 cells overexpressing VEGF₁₂₁b or VEGF₁₆₅b (or carrying the PCDNA3.1 empty vector, as control) and xenotransplanted into nude mice showed increased tumor volume and angiogenesis compared to controls. To assess whether the VEGF(xxx)b isoforms are differentially expressed in tumors compared to healthy tissues, immunohistochemical analysis was conducted on a breast cancer tissue microarray. A significant increase (p < 0.05) in both VEGF(xxx)b and total VEGF-A protein expression in infiltrating ductal carcinomas compared to normal breasts was observed. A positive significant correlation (r = 0.404, p = 0.033) between VEGF(xxx)b and total VEGF-A was found.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b are not anti-angiogenic, but weakly angiogenic isoforms of VEGF-A. In addition, VEGF(xxx)b isoforms are up-regulated in breast cancer in comparison with non malignant breast tissues. These results are to be taken into account when considering a possible use of VEGF₁₂₁/₁₆₅b-based therapies in patients.
Figures

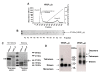




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

