Noninvasive treatment of deep venous thrombosis using pulsed ultrasound cavitation therapy (histotripsy) in a porcine model
- PMID: 21194969
- PMCID: PMC3053086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2010.10.007
Noninvasive treatment of deep venous thrombosis using pulsed ultrasound cavitation therapy (histotripsy) in a porcine model
Abstract
Purpose: This study evaluated histotripsy as a noninvasive, image-guided method of thrombolysis in a porcine model of deep vein thrombosis. Histotripsy therapy uses short, high-intensity, focused ultrasound pulses to cause mechanical breakdown of targeted soft tissue by acoustic cavitation, which is guided by real-time ultrasound imaging. This is an in vivo feasibility study of histotripsy thrombolysis.
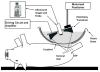
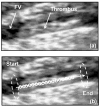
Methods and materials: Acute thrombi were formed in the femoral vein of juvenile pigs weighing 30-40 kg by balloon occlusion with two catheters and thrombin infusion. A 10-cm-diameter 1-MHz focused transducer was used for therapy. An 8-MHz ultrasound imager was used to align the clot with the therapy focus. Therapy consisted of five cycle pulses delivered at a rate of 1 kHz and peak negative pressure between 14 and 19 MPa. The focus was scanned along the long axis of the vessel to treat the entire visible clot during ultrasound exposure. The targeted region identified by a hyperechoic cavitation bubble cloud was visualized via ultrasound during treatment.
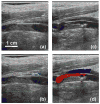
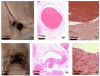
Results: Thrombus breakdown was apparent as a decrease in echogenicity within the vessel in 10 of 12 cases and in 7 cases improved flow through the vein as measured by color Doppler. Vessel histology found denudation of vascular endothelium and small pockets of hemorrhage in the vessel adventitia and underlying muscle and fatty tissue, but perforation of the vessel wall was never observed.
Conclusions: The results indicate histotripsy has potential for development as a noninvasive treatment for deep vein thrombosis.
Copyright © 2011 SIR. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have any affiliations with industry or conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Motykie GD, Zebala LP, Caprini JA, et al. A guide to venous thromboembolism risk factor assessment. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2000;9:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Lensing AWA, Prandoni P, Prins MH, Büller HR. Deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1999;353:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Sharafuddin MJ, Sun S, Hoballah JJ, Youness FM, Sharp WJ, Roh B-S. Endovascular management of venous thrombotic and occlusive diseases of the lower extremities. J Vasc and Interv Radiol. 2003;14:405–423. - PubMed
-
- Comerota AJ, Paolini D. Treatment of acute iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis: A strategy of thrombus removal. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:640–640. - PubMed
-
- Markel A, Manzo RA, Bergelin RO, Strandness DE., Jr Valvular reflux after deep vein thrombosis: incidence and time of occurrence. J Vasc Surg. 1992;15:377–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

