Activated expression of cardiac adenylyl cyclase 6 reduces dilation and dysfunction of the pressure-overloaded heart
- PMID: 21195051
- PMCID: PMC3219303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.113
Activated expression of cardiac adenylyl cyclase 6 reduces dilation and dysfunction of the pressure-overloaded heart
Abstract
Background and objective: Cardiac-directed adenylyl cyclase 6 (AC6) expression attenuates left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and dysfunction in cardiomyopathy, but its effects in the pressure-overloaded heart are unknown.
Methods: Mice with cardiac-directed and regulated expression of AC6 underwent transaortic constriction (TAC) to induce LV pressure overload. Ten days prior to TAC, and for the duration of the 4 week study, cardiac myocyte AC6 expression was activated in one group (AC-On) but not the other (AC-Off). Multiple measures of LV systolic and diastolic function were obtained 4 weeks after TAC, and LV samples assessed for alterations in Ca2+ signaling.
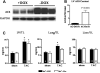
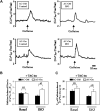
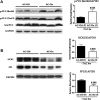
Results: LV contractility, as reflected in the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Emax), was increased (p=0.01) by activation of AC6 expression. In addition, diastolic function was improved (p<0.05) and LV dilation was reduced (p<0.05). LV samples from AC-On mice showed reduced protein expression of sodium/calcium exchanger (NCX1) (p<0.05), protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) (p<0.01), and increased phosphorylation of phospholamban (PLN) at Ser16 (p<0.05). Finally, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ content was increased in cardiac myocytes isolated from AC-On mice (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Activation of cardiac AC6 expression improves function of the pressure-overloaded and failing heart. The predominant mechanism for this favorable adaptation is improved Ca2+ handling, a consequence of increased PLN phosphorylation, reduced NCX1, reduced PP1 expression, and increased SR Ca2+ content.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
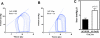
References
-
- Antos CL, Frey N, Marx SO, Reiken S, Gaburjakova M, Richardson JA, Marks AR, Olson EN. Dilated cardiomyopathy and sudden death resulting from constitutive activation of protein kinase a. Circ. Res. 2001;89:997–1004. - PubMed
-
- Roth DM, Bayat H, Drumm JD, Gao MH, Swaney JS, Ander A, Hammond HK. Adenylyl cyclase increases survival in cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2002;105:1989–1994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

