L2pB1: a new player in autoimmunity
- PMID: 21195478
- PMCID: PMC3087825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.12.006
L2pB1: a new player in autoimmunity
Abstract
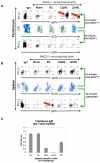
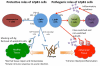
L2pB1 cells (PD-L2positive B1 cells) are a newly discovered subpopulation of B1 B cells. L2pB1 cells are noted for the expression of PD-L2 (CD273, B7-DC), a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PD-1, which distinguishes this subpopulation from other B1 B cells that lack PD-L2, namely, L2nB1 cells (PD-L2negative B1 cells). PD-L2 gene expression is regulated differently in B1 B cells as compared to macrophages and dendritic cells. L2pB1 cells share many commonly known B1 cell features with L2nB1 cells. These include spontaneous IgM secretion, constitutive ERK activation, elevated co-stimulatory molecule expression, skewing of T cell differentiation, and unique proliferative responsiveness (to LPS, PMA, but not anti-IgM). However, L2pB1 cells express a biased Ig repertoire that is enriched for self-reactivity as compared with L2nB1 cells. Further, L2pB1 cells present antigen more potently than L2nB1 cells. In addition, L2pB1 cells switch Ig isotype more readily from IgM to IgG1 and IgG2b upon cytokine stimulation. Moreover, increased numbers of L2pB1 cells are present in murine models of lupus and this correlates with increased serum anti-dsDNA titers. These characteristics suggest that L2pB1 cells may play a pathophysiological role in autoimmune dyscrasias. In this report we review the special features of L2pB1 cells and how they may contribute to autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Amel Kashipaz MR, Huggins ML, Lanyon P, Robins A, Powell RJ, Todd I. Assessment of Be1 and Be2 cells in systemic lupus erythematosus indicates elevated interleukin-10 producing CD5+ B cells. Lupus. 2003;12:356–63. - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Harris RB, Cyster JG. CXCL13 is required for B1 cell homing, natural antibody production, and body cavity immunity. Immunity. 2002;16:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Baudino L, Nimmerjahn F, Azeredo da Silveira S, Martinez-Soria E, Saito T, Carroll M, Ravetch JV, Verbeek JS, Izui S. Differential contribution of three activating IgG Fc receptors (FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, and FcgammaRIV) to IgG2a-and IgG2b-induced autoimmune hemolytic anemia in mice. J Immunol. 2008;180:1948–53. - PubMed
-
- Becker H, Weber C, Storch S, Federlin K. Relationship between CD5+ B lymphocytes and the activity of systemic autoimmunity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990;56:219–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

