Epithelial and mesenchymal phenotypic switchings modulate cell motility in metastasis
- PMID: 21196205
- PMCID: PMC4003907
- DOI: 10.2741/3722
Epithelial and mesenchymal phenotypic switchings modulate cell motility in metastasis
Abstract
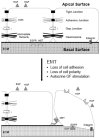
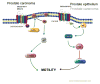
The most ominous stage of cancer progression is metastasis, or the dissemination of carcinoma cells from the primary site into distant organs. Metastases are often resistant to current extirpative therapies and even the newest biological agents cure only a small subset of patients. Therefore a greater understanding of tumor biology that integrates properties intrinsic to carcinomas with tissue environmental modulators of behavior is needed. In no aspect of tumor progression is this more evident than the acquisition of cell motility that is critical for both escape from the primary tumor and colonization. In this overview, we discuss how this behavior is modified by carcinoma cell phenotypic plasticity that is evidenced by reversible switching between epithelial and mesenchymal phenotypes. The presence or absence of intercellular adhesions mediate these switches and dictate the receptivity towards signals from the extracellular milieu. These signals, which include soluble growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular matrix embedded with matrikines and matricryptines will be discussed in depth. Finally, we will describe a new mode of discerning the balance between epithelioid and mesenchymal movement.
Figures


References
-
- Thompson EW, Newgreen DF. Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Research. 2005;65(14):5991–5995. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen JJ, Rajasekaran AK. Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Research. 2006;66(17):8319–8326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

