Hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta due to WDR72 mutations: a novel mutation and ultrastructural analyses of deciduous teeth
- PMID: 21196691
- PMCID: PMC3128158
- DOI: 10.1159/000322036
Hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta due to WDR72 mutations: a novel mutation and ultrastructural analyses of deciduous teeth
Abstract
Background: Mutations in WDR72 have been identified in autosomal recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta (AI).
Objective: to describe a novel WDR72 mutation and report the ultrastructural enamel phenotype associated with a different WDR72 mutation.
Methods: A family segregating autosomal recessive hypomaturation AI was recruited, genomic DNA obtained and WDR72 sequenced. Four deciduous teeth from one individual with a previously published WDR72 mutation, extracted as part of clinical care, were subjected to scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis and transverse microradiography.
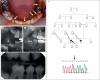
Results: A novel homozygous nonsense mutation, R897X, was identified in WDR72 in a family originating from Pakistan. Ultrastructural analysis of enamel from the deciduous teeth of an AI patient with the WDR72 mutation S783X revealed energy-dispersive X-ray analysis spectra with normal carbon and nitrogen peaks, excluding retention of enamel matrix protein. However, transverse microradiography values were significantly lower for affected teeth when compared to normal teeth, consistent with reduced mineralisation. On scanning electron microscopy the enamel rod form observed was normal, yet with inter-rod enamel more prominent than in controls. This appearance was unaltered following incubation with either α-chymotrypsin or lipase.
Conclusions: The novel WDR72 mutation described brings the total reported WDR72 mutations to four. Analyses of deciduous tooth enamel in an individual with a homozygous WDR72 mutation identified changes consistent with a late failure of enamel maturation without retention of matrix proteins. The mechanisms by which intracellular WDR72 influences enamel maturation remain unknown.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Hashimi N., Sire J.Y., Delgado S. Evolutionary analysis of mammalian enamelin, the largest enamel protein, supports a crucial role for the 32-kDa peptide and reveals selective adaptation in rodents and primates. J Mol Evol. 2009;69:635–656. - PubMed
-
- Aldred M.J., Savarirayan R., Crawford P.J. Amelogenesis imperfecta: a classification and catalogue for the 21st century. Oral Dis. 2003;9:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Barron M.J., Brookes S.J., Kirkham J., Shore R.C., Hunt C., Mironov A., Kingswell N.J., Maycock J., Shuttleworth C.A., Dixon M.J. A mutation in the mouse Amelx tri-tyrosyl domain results in impaired secretion of amelogenin and phenocopies human X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:1230–1247. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyde A. Enamel. In: Oksche A, Vollrath L, editors. Handbook of Microscopic Anatomy. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1989. pp. 309–473.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

