Proximal tubule cell hypothesis for cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes
- PMID: 21197105
- PMCID: PMC3005801
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/957164
Proximal tubule cell hypothesis for cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes
Abstract
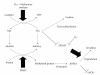
Incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) is remarkably high among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), even in the early microalbuminuric stages with normal glomerular filtration rates. Proximal tubule cells (PTCs) mediate metabolism and urinary excretion of vasculotoxic substances via apical and basolateral receptors and transporters. These cells also retrieve vasculoprotective substances from circulation or synthesize them for release into the circulation. PTCs are also involved in the uptake of sodium and phosphate, which are critical for hemodynamic regulation and maintaining the mineral balance, respectively. Dysregulation of PTC functions in CKD is likely to be associated with the development of CVD and is linked to the progression to end-stage renal disease. In particular, PTC dysfunction occurs early in diabetic nephropathy, a leading cause of CKD. It is therefore important to elucidate the mechanisms of PTC dysfunction to develop therapeutic strategies for treating cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes.
Figures

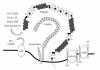
Similar articles
-
SGLT2 Inhibition for CKD and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: Report of a Scientific Workshop Sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Jan;77(1):94-109. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.08.003. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33121838
-
[Electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders in advanced chronic kidney disease].Nefrologia. 2008;28 Suppl 3:87-93. Nefrologia. 2008. PMID: 19018744 Spanish.
-
[Regulation of natriuresis in diabetic nephropathy].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2000;46:241-52. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2000. PMID: 11712308 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and prevention of diabetic nephropathy: targeting the renal tubule in diabetes.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jul;64(1):16-24. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24673844 Review.
-
Role of megalin, a proximal tubular endocytic receptor, in the pathogenesis of diabetic and metabolic syndrome-related nephropathies: protein metabolic overload hypothesis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2005 Oct;10 Suppl:S26-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00453.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005. PMID: 16174284 Review.
Cited by
-
The Envy of Scholars: Applying the Lessons of the Framingham Heart Study to the Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease.Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2015 Jul 30;6(3):e0029. doi: 10.5041/RMMJ.10214. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2015. PMID: 26241225 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of Ketone Bodies in the Evaluation of Kidney Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Apr 10;2021:5596125. doi: 10.1155/2021/5596125. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 33937415 Free PMC article.
-
Less known pathophysiological mechanisms of anemia in patients with diabetic nephropathy.Int Urol Nephrol. 2015 Aug;47(8):1365-72. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1012-2. Epub 2015 May 28. Int Urol Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26017902 Review.
-
Efficacy of Urine Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Concentration to Predict Azotemia in Hyperthyroid Cats After Radio-Iodine Treatment.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 May-Jun;39(3):e70096. doi: 10.1111/jvim.70096. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40271736 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 22;12(4):773. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040773. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerstein HC, Mann JFE, Yi Q, et al. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2001;286(4):421–426. - PubMed
-
- Wachtell K, Ibsen H, Olsen MH, et al. Albuminuria and cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the LIFE study. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2003;139(11):901–906. - PubMed
-
- KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Kidney International. 2009;113:S1–S130. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, Burns WC, Cooper ME. Tubular changes in early diabetic nephropathy. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. 2005;12(2):177–186. - PubMed
-
- Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: a final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2006;17(1):17–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

