Accidental salinomycin intoxication in calves
- PMID: 21197208
- PMCID: PMC2942056
Accidental salinomycin intoxication in calves
Abstract
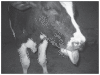
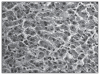
Twenty-four 10- to 16-week-old calves in a dairy herd in Birjand, Iran, inadvertently received an excessive dose of salinomycin mixed with barley grain. There was 58% mortality within 10 d. The calves had high serum AST, LDH, and CK activities; histopathologic lesions in myocardium, liver, and kidneys; and clinical signs associated with acute and congestive heart failure.
Intoxication accidentelle à la salinomycine chez des veaux. Vingt-quatre veaux âgés de 10 à 16 semaines faisant partie d’un troupeau laitier de Birjand, en Iran, ont reçu par inadvertance une dose excessive de salinomycine mélangée avec du grain d’orge. Il s’est produit une mortalité de 58 % dans un délai de 10 jours. Les veaux présentaient des activités sériques SGOT, LDH et CK élevées, des lésions histopathologiques du myocarde, du foie et des reins et des signes cliniques associés à une insuffisance cardiaque congestive.
(Traduit par Isabelle Vallières)
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salinomycin toxicity in dairy calves.Vet Rec. 2011 Nov 19;169(21):561. doi: 10.1136/vr.d7423. Vet Rec. 2011. PMID: 22102355 No abstract available.
-
Salinomycin toxicity in pigs.Vet Rec. 1990 Nov 17;127(20):507. Vet Rec. 1990. PMID: 2275094 No abstract available.
-
Salinomycin poisoning in point-of-lay turkeys.Aust Vet J. 1989 Oct;66(10):326-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1989.tb09718.x. Aust Vet J. 1989. PMID: 2818361
-
Ionophore use and toxicosis in cattle.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2000 Nov;16(3):497-509, vii. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30083-9. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2000. PMID: 11084989 Review.
-
Salinomycin toxicity causes deaths of calves on two Scottish dairy farms.Vet Rec. 2012 Feb 4;170(5):118-21. doi: 10.1136/vr.e705. Vet Rec. 2012. PMID: 22416283 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
High mortality due to accidental salinomycin intoxication in sheep.Interdiscip Toxicol. 2014 Sep;7(3):173-6. doi: 10.2478/intox-2014-0024. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 26109896 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent adverse effects of salinomycin on male reproductive organs and fertility in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 1;8(7):e69086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069086. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840907 Free PMC article.
-
Salinomycin efficiency assessment in non-tumor (HB4a) and tumor (MCF-7) human breast cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;389(6):557-71. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1225-7. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26932586
-
Dissecting pharmacological effects of chloroquine in cancer treatment: interference with inflammatory signaling pathways.Immunology. 2020 Mar;159(3):257-278. doi: 10.1111/imm.13160. Epub 2019 Dec 22. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 31782148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concomitant Delivery of Pirarubicin and Salinomycin Synergistically Enhanced the Efficacy of Cancer Therapy and Reduced the Risk of Cancer Relapse.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Sep 7;25(7):211. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02918-3. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39242397
References
-
- Bergen WG, Bates DB. Ionophores: Their effect on production efficiency and mode of action. J Anim Sci. 1984;58:1465–1483. - PubMed
-
- Novilla MN. The veterinary importance of the toxic syndrome induced by ionophores. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1992;34:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Radostits OM, Gay CC, Hinchcliff KW, Constable PD. Veterinary Medicine. 10th ed. London: Saunders & Elsevier; 2007. pp. 1844–1846.
-
- Russell JB, Houlihan AJ. Ionophore resistance of ruminal bacteria and its potential impact on human health. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2003;27:65–74. - PubMed
-
- Novilla MN. Ionophores. In: Gupta RC, editor. Veterinary Toxicology — Basic and Clinical Principles. Amsterdam: Elsevier-AP; 2007. pp. 1021–1041.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
