Experimental ablation of the pancreas with high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in a porcine model
- PMID: 21197259
- PMCID: PMC3005545
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.8.9
Experimental ablation of the pancreas with high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in a porcine model
Abstract
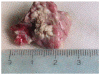
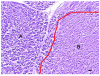
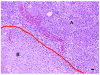
The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility and safety of high intensity focused ultrasound's (HIFU) in pancreatic diseases. Twelve pigs were divided into three groups. The pancreases of pigs in Group A were ablated directly with HIFU, but those in Group B and C ablated by extracorporeal HIFU. The pigs in Group C were sacrificed at day 7 after HIFU. Serological parameters were determined pre-operation and post-operation. The entire pancreas was removed for histological examination. Each animal tolerate the HIFU ablation well. The complete necrosis was observed in targeted regions. The margins of the necrotic regions were clearly delineated from the surrounding normal tissues. Infiltration of inflammatory cells and phorocytosis on the boundary were found in group C. Blood and urine amylase levels were relatively steady after HIFU. No acute pancreatitis or severe complications occurred. In conclusion, HIFU ablation on the pancreas was safe and effective in experimental pigs.
Keywords: Ablation.; High intensity focused ultrasound; Pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thermal Ablation of the Pancreas With Intraoperative High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound: Safety and Efficacy in a Porcine Model.Pancreas. 2017 Feb;46(2):219-224. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000720. Pancreas. 2017. PMID: 27841792
-
Preclinical in vivo evaluation of an extracorporeal HIFU device for ablation of pancreatic tumors.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009 Jun;35(6):967-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.12.006. Epub 2009 Feb 8. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19201519
-
Experimental study in vivo ablation of swine pancreas using high-intensity focused ultrasound.J Cancer Res Ther. 2019;15(2):286-290. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_986_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30964099
-
High intensity focused ultrasound: a noninvasive therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 28;20(44):16480-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16480. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25469016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal ablation of liver tissue by high-intensity focused ultrasound.Oncology. 1993 Sep-Oct;50(5):375-9. doi: 10.1159/000227213. Oncology. 1993. PMID: 8378034 Review.
Cited by
-
HIFU for palliative treatment of pancreatic cancer.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011 Sep;2(3):175-84. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2011.033. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22811848 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative HIFU Ablation of the Pancreas Using a Toroidal Transducer in a Porcine Model. The First Step towards a Clinical Treatment of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;13(24):6381. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246381. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34945001 Free PMC article.
-
Focused Ultrasound for Immunomodulation of the Tumor Microenvironment.J Immunol. 2020 Nov 1;205(9):2327-2341. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901430. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33077668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an acute pancreatitis porcine model based on endoscopic retrograde infusion of contrast medium or sodium taurocholate.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 Nov;34(6):1244-1251. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.367. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30428647 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapeutic Method for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer-The Impact of the Long-Term Research in Therapeutic Effect of High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Therapy.Curr Oncol. 2021 Nov 20;28(6):4845-4861. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28060409. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34898585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Burov AK. High-intensity ultrasonic vibrations for action on animal and human malignant tumors. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1956;106:239–41.
-
- Wu F. Extracorporeal high intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of patients with solid malignancy. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2006;15:26–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

