Layers of epistasis: genome-wide regulatory networks and network approaches to genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 21197657
- PMCID: PMC3062944
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.132
Layers of epistasis: genome-wide regulatory networks and network approaches to genome-wide association studies
Abstract
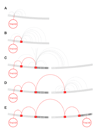
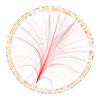
The conceptual foundation of the genome-wide association study (GWAS) has advanced unchecked since its conception. A revision might seem premature as the potential of GWAS has not been fully realized. Multiple technical and practical limitations need to be overcome before GWAS can be fairly criticized. But with the completion of hundreds of studies and a deeper understanding of the genetic architecture of disease, warnings are being raised. The results compiled to date indicate that risk-associated variants lie predominantly in noncoding regions of the genome. Additionally, alternative methodologies are uncovering large and heterogeneous sets of rare variants underlying disease. The fear is that, even in its fulfillment, the current GWAS paradigm might be incapable of dissecting all kinds of phenotypes. In the following text, we review several initiatives that aim to overcome these limitations. The overarching theme of these studies is the inclusion of biological knowledge to both the analysis and interpretation of genotyping data. GWAS is uninformed of biology by design and although there is some virtue in its simplicity, it is also its most conspicuous deficiency. We propose a framework in which to integrate these novel approaches, both empirical and theoretical, in the form of a genome-wide regulatory network (GWRN). By processing experimental data into networks, emerging data types based on chromatin immunoprecipitation are made computationally tractable. This will give GWAS re-analysis efforts the most current and relevant substrates, and root them firmly on our knowledge of human disease.
Copyright © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Andrew AS, Nelson HH, Kelsey KT, Moore JH, Meng AC, Casella DP, Tosteson TD, Schned AR, Karagas MR. Concordance of multiple analytical approaches demonstrates a complex relationship between dna repair gene snps, smoking and bladder cancer susceptibility. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(5):1030–1037. - PubMed
-
- Askland K, Read C, Moore J. Pathways-based analyses of whole-genome association study data in bipolar disorder reveal genes mediating ion channel activity and synaptic neurotransmission. Hum Genet. 2009;125(1):63–79. - PubMed
-
- Bobadilla JL, Macek M, Fine JP, Farrell PM. Cystic fibrosis: a worldwide analysis of cftr mutations–correlation with incidence data and application to screening. Hum Mutat. 2002;19(6):575–606. - PubMed
-
- Bucan M, Abrahams BS, Wang K, Glessner JT, Herman EI, Sonnenblick LI, Retuerto AIA, Imielinski M, Hadley D, Bradfield JP, Kim C, Gidaya NB, Lindquist I, Hutman T, Sigman M, Kustanovich V, Lajonchere CM, Singleton A, Kim J, Wassink TH, McMahon WM, Owley T, Sweeney JA, Coon H, Nurnberger JI, Li M, Cantor RM, Minshew NJ, Sutcliffe JS, Cook EH, Dawson G, Buxbaum JD, Grant SFA, Schellenberg GD, Geschwind DH, Hakonarson H. Genome-wide analyses of exonic copy number variants in a family-based study point to novel autism susceptibility genes. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(6):e1000536. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan CS, Song JS. Ccctc-binding factor confines the distal action of estrogen receptor. Cancer Research. 2008;68(21):9041–9049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

