Impact of species variability and 'probe-dependence' on the detection and in vivo validation of allosteric modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
- PMID: 21198541
- PMCID: PMC3057301
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01184.x
Impact of species variability and 'probe-dependence' on the detection and in vivo validation of allosteric modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Abstract
Background and purpose: We recently characterized LY2033298 as a novel allosteric modulator and agonist at M(4) muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). Evidence also suggested a difference in the potency of LY2033298 at rodent relative to human M(4) mAChRs. The current study investigated the basis for the species difference of this modulator and used this knowledge to rationalize its in vivo actions.
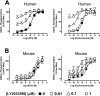
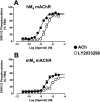
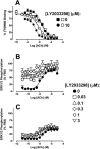
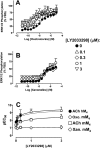
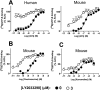
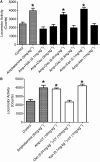
Experimental approach: LY2033298 was investigated in vitro in CHO cells stably expressing human or mouse M(4) mAChRs, using assays of agonist-induced ERK1/2 or GSK-3α phosphorylation, [(35) S]-GTPγS binding, or effects on equilibrium binding of [(3) H]-NMS and ACh. The in vivo actions of LY2033298 were investigated in a mouse model of amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. The function of LY2033298 was examined in combination with ACh, oxotremorine or xanomeline.
Key results: LY2033298 had similar affinities for the human and mouse M(4) mAChRs. However, LY2033298 had a lower positive co-operativity with ACh at the mouse relative to the human M(4) mAChR. At the mouse M(4) mAChR, LY2033298 showed higher co-operativity with oxotremorine than with ACh or xanomeline. The different degrees of co-operativity between LY2033298 and each agonist at the mouse relative to the human M(4) mAChR necessitated the co-administration of LY2033298 with oxotremorine in order to show in vivo efficacy of LY2033298.
Conclusions and implications: These results provide evidence for species variability when comparing the allosteric interaction between LY2033298 and ACh at the M(4) mAChR, and also highlight how the interaction between LY2033298 and different orthosteric ligands is subject to 'probe dependence'. This has implications for the validation of allosteric modulator actions in vivo.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Aurelio L, Valant C, Flynn BL, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A, Scammels PJ. Allosteric modulators of the adenosine A1 receptor: synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 4-Substituted 2-Amino-3-benzoylthiophenes. J Med Chem. 2009;52:4543–4547. - PubMed
-
- Black JW, Leff P. Operational Models of Pharmacological Agonism. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983;220:141–162. - PubMed
-
- Buckley P, Stahl SM. Pharmacological treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia: therapeutic opportunity or Cul-de-sac? Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2007;115:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

