Cutting edge: TIGIT has T cell-intrinsic inhibitory functions
- PMID: 21199897
- PMCID: PMC3128994
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003081
Cutting edge: TIGIT has T cell-intrinsic inhibitory functions
Abstract
Costimulatory molecules regulate the functional outcome of T cell activation, and disturbance of the balance between activating and inhibitory signals results in increased susceptibility to infection or the induction of autoimmunity. Similar to the well-characterized CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory pathway, a newly emerging pathway consisting of CD226 and T cell Ig and ITIM domain (TIGIT) has been associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. In this study, we examined the role of the putative coinhibitory molecule TIGIT and show that loss of TIGIT in mice results in hyperproliferative T cell responses and increased susceptibility to autoimmunity. TIGIT is thought to indirectly inhibit T cell responses by the induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells. By generating an agonistic anti-TIGIT Ab, we demonstrate that TIGIT can inhibit T cell responses directly independent of APCs. Microarray analysis of T cells stimulated with agonistic anti-TIGIT Ab revealed that TIGIT can act directly on T cells by attenuating TCR-driven activation signals.
Figures



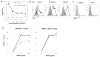
References
-
- Hafler JP, Maier LM, Cooper JD, Plagnol V, Hinks A, Simmonds MJ, Stevens HE, Walker NM, Healy B, Howson JM, Maisuria M, Duley S, Coleman G, Gough SC, Worthington J, Kuchroo VK, Wicker LS, Todd JA. CD226 Gly307Ser association with multiple autoimmune diseases. Genes Immun. 2009;10:5–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tahara-Hanaoka S, Shibuya K, Onoda Y, Zhang H, Yamazaki S, Miyamoto A, Honda S, Lanier LL, Shibuya A. Functional characterization of DNAM-1 (CD226) interaction with its ligands PVR (CD155) and nectin-2 (PRR-2/CD112) Int Immunol. 2004;16:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Harden K, Gonzalez LC, Francesco M, Chiang E, Irving B, Tom I, Ivelja S, Refino CJ, Clark H, Eaton D, Grogan JL. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:48–57. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Irizarry RA, Gentleman R, Martinez-Murillo F, Spencer F. A Model-Based Background Adjustment for Oligonucleotide Expression Arrays. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2004;99:909–917.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

