Continuous-time model of structural balance
- PMID: 21199953
- PMCID: PMC3033300
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1013213108
Continuous-time model of structural balance
Abstract
It is not uncommon for certain social networks to divide into two opposing camps in response to stress. This happens, for example, in networks of political parties during winner-takes-all elections, in networks of companies competing to establish technical standards, and in networks of nations faced with mounting threats of war. A simple model for these two-sided separations is the dynamical system dX/dt = X(2), where X is a matrix of the friendliness or unfriendliness between pairs of nodes in the network. Previous simulations suggested that only two types of behavior were possible for this system: Either all relationships become friendly or two hostile factions emerge. Here we prove that for generic initial conditions, these are indeed the only possible outcomes. Our analysis yields a closed-form expression for faction membership as a function of the initial conditions and implies that the initial amount of friendliness in large social networks (started from random initial conditions) determines whether they will end up in intractable conflict or global harmony.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
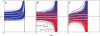
 for B and C using estimates of λ1 taken from ref. . The black dotted lines mark the blow-up times t∗ = 1/(cλ1).
for B and C using estimates of λ1 taken from ref. . The black dotted lines mark the blow-up times t∗ = 1/(cλ1).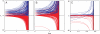
Comment in
-
Local balancing influences global structure in social networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):1751-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018901108. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21252302 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Community detectability and structural balance dynamics in signed networks.Phys Rev E. 2020 Jul;102(1-1):012304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.102.012304. Phys Rev E. 2020. PMID: 32795056
-
Dynamics of opinion forming in structurally balanced social networks.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038135. Epub 2012 Jun 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761667 Free PMC article.
-
The structural balance analysis of complex dynamical networks based on nodes' dynamical couplings.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 31;13(1):e0191941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191941. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29385183 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamical models explaining social balance and evolution of cooperation.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 25;8(4):e60063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060063. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23634204 Free PMC article.
-
[The Gulf War Syndrome twenty years on].Encephale. 2013 Oct;39(5):332-8. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.11.003. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23351934 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The evolution of cooperation in signed networks under the impact of structural balance.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 8;13(10):e0205084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205084. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30296278 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional attributes expose Heider balance dynamics to measurements.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 20;13(1):15568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42390-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37730884 Free PMC article.
-
Market Choices Driven by Reference Groups: A Comparison of Analytical and Simulation Results on Random Networks.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Aug 1;23(8):1007. doi: 10.3390/e23081007. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441147 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of Disagreement: Large-Scale Temporal Network Analysis Reveals Negative Interactions in Online Collaboration.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 3;6:36333. doi: 10.1038/srep36333. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27808267 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionary game approach for determination of the structural conflicts in signed networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 26;6:22022. doi: 10.1038/srep22022. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26915581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wasserman S, Faust K. Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications, Structural Analysis in the Social Sciences. New York: Cambridge Univ Press; 1994. pp. 220–248.
-
- Heider F. Attitudes and cognitive organization. J Psychol. 1946;21:107–112. - PubMed
-
- Cartwright D, Harary F. Structural balance: A generalization of Heider’s theory. Psychol Rev. 1956;63:277–293. - PubMed
-
- Antal T, Krapivsky PL, Redner S. Dynamics of social balance on networks. Phys Rev E. 2005;72:036121. - PubMed
-
- Marvel SA, Strogatz SH, Kleinberg JM. Energy landscape of social balance. Phys Rev Lett. 2009;103:198701. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

