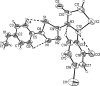
2-(2,4-Dichloro-phen-yl)-3-[5-(4-methoxy-phen-yl)-1,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl]-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one
- PMID: 21202287
- PMCID: PMC2961251
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808008465
2-(2,4-Dichloro-phen-yl)-3-[5-(4-methoxy-phen-yl)-1,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl]-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one
Abstract
In the mol-ecule of the title compound, C(18)H(13)Cl(2)N(3)O(2)S(2), the thia-zolidinone ring has an envelope conformation with the S atom displaced by 0.394 (3) Å from the plane of the other ring atoms. The thia-diazole ring is oriented at a dihedral angle of 7.40 (4)° with respect to the 4-methoxy-phenyl ring. Intra-molecular C-H⋯S, C-H⋯N and C-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds result in the formation of two planar and two non-planar five-membered rings. The planar five-membered rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 6.23 (3)°. The 2,4-dichloro-phenyl ring is oriented at dihedral angles of 84.21 (4) and 83.55 (3)° with respect to the thia-diazole and 4-methoxy-phenyl rings, respectively. In the crystal structure, inter-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into centrosymmetric dimers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2-Meth-oxy-N-[5-(2-methoxy-phen-yl)-1,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl]benzamide hemi-hydrate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008 Jul 31;64(Pt 8):o1637. doi: 10.1107/S1600536808019934. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008. PMID: 21203326 Free PMC article.
-
3-[5-(4-Fluoro-phen-yl)-1,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl]-2-(4-methoxy-phen-yl)-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008 Jun 28;64(Pt 7):o1359. doi: 10.1107/S1600536808019089. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008. PMID: 21202977 Free PMC article.
-
1-(4-Isopropyl-phen-yl)-5-(4-methoxy-phen-yl)pyrazolidin-3-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008 Apr 16;64(Pt 5):o855. doi: 10.1107/S1600536808009823. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008. PMID: 21202342 Free PMC article.
-
2-(4-Fluoro-phen-yl)-3-[5-(4-nitro-phen-yl)-1,3,4-thia-diazol-2-yl]-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 Jun 23;66(Pt 7):o1737. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810023354. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21587954 Free PMC article.
-
6-(4-Pyrid-yl)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phen-yl)-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thia-diazole.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008 Jul 31;64(Pt 8):o1634. doi: 10.1107/S1600536808023544. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2008. PMID: 21203323 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of (2Z,5Z)-3-(4-meth-oxy-phen-yl)-2-[(4-meth-oxy-phenyl)-imino]-5-[(E)-3-(2-nitro-phen-yl)allyl-idene]-1,3-thia-zolidin-4-one.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2016 Jan 13;72(Pt 2):155-7. doi: 10.1107/S2056989016000207. eCollection 2016 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2016. PMID: 26958377 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of ethyl 2-{[4-ethyl-5-(quinolin-8-yloxymeth-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]sulfan-yl}acetate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Jan 13;73(Pt 2):173-176. doi: 10.1107/S205698901700041X. eCollection 2017 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017. PMID: 28217336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arun, K. P., Nag, V. L. & Panda, C. S. (1999). Indian J. Chem.38B, 998–1001.
-
- Chen, H. S., Li, Z. M. & Han, Y. F. (2000). J. Agric. Food Chem.48, 5312–5315. - PubMed
-
- Enraf–Nonius (1989). CAD-4 Software Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
-
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1995). XCAD4 University of Marburg, Germany.
-
- Kidwai, M., Negi, N. & Misra, P. (2000). J. Indian Chem. Soc.77, 46–48.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources