Pharmacological treatment of painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 21203440
- PMCID: PMC3010990
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014433
Pharmacological treatment of painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Significant pain from HIV-associated sensory neuropathy (HIV-SN) affects ∼40% of HIV infected individuals treated with antiretroviral therapy (ART). The prevalence of HIV-SN has increased despite the more widespread use of ART. With the global HIV prevalence estimated at 33 million, and with infected individuals gaining increased access to ART, painful HIV-SN represents a large and expanding world health problem. There is an urgent need to develop effective pain management strategies for this condition.
Objective: To evaluate the clinical effectiveness of analgesics in treating painful HIV-SN.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data sources: Medline, Cochrane central register of controlled trials, www.clinicaltrials.gov, www.controlled-trials.com and the reference lists of retrieved articles.
Selection criteria: Prospective, double-blinded, randomised controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the pharmacological treatment of painful HIV-SN with sufficient quality assessed using a modified Jadad scoring method.
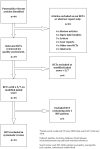
Review methods: Four authors assessed the eligibility of articles for inclusion. Agreement of inclusion was reached by consensus and arbitration. Two authors conducted data extraction and analysis. Dichotomous outcome measures (≥ 30% and ≥ 50% pain reduction) were sought from RCTs reporting interventions with statistically significant efficacies greater than placebo. These data were used to calculate RR and NNT values.
Results: Of 44 studies identified, 19 were RCTs. Of these, 14 fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Interventions demonstrating greater efficacy than placebo were smoked cannabis NNT 3.38 95%CI(1.38 to 4.10), topical capsaicin 8%, and recombinant human nerve growth factor (rhNGF). No superiority over placebo was reported in RCTs that examined amitriptyline (100mg/day), gabapentin (2.4 g/day), pregabalin (1200 mg/day), prosaptide (16 mg/day), peptide-T (6 mg/day), acetyl-L-carnitine (1g/day), mexilitine (600 mg/day), lamotrigine (600 mg/day) and topical capsaicin (0.075% q.d.s.).
Conclusions: Evidence of efficacy exists only for capsaicin 8%, smoked cannabis and rhNGF. However,rhNGF is clinically unavailable and smoked cannabis cannot be recommended as routine therapy. Evaluation of novel management strategies for painful HIV-SN is urgently needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Smyth K, Affandi JS, McArthur JC, Bowtell-Harris C, Mijch AM, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for HIV-associated neuropathy in Melbourne, Australia 1993–2006. HIV Med. 2007;8:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Lipkin WI, Parry G, Kiprov D, Abrams D. Inflammatory neuropathy in homosexual men with lymphadenopathy. Neurology. 1985;35:1479–1483. - PubMed
-
- Barohn R, Gronseth G, Leforce B, McVey A, McGuire A, et al. Peripheral nerve involvement in a large cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Arch Neurol. 1993;50:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Blum AS, Dal Pan GJ, Feinberg J, Raines C, Mayjo K, et al. Low-dose zalcitabine-related toxic neuropathy: frequency, natural history, and risk factors. Neurology. 1996;46:999–1003. - PubMed
-
- Yarchoan R, Perno CF, Thomas RV, Klecker RW, Allain JP, et al. Phase I studies of 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine in severe human immunodeficiency virus infection as a single agent and alternating with zidovudine (AZT). Lancet. 1988;1:76–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical