Hsp72 is an early and sensitive biomarker to detect acute kidney injury
- PMID: 21204265
- PMCID: PMC3401998
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.201000105
Hsp72 is an early and sensitive biomarker to detect acute kidney injury
Abstract
This study was designed to assess whether heat shock protein Hsp72 is an early and sensitive biomarker of acute kidney injury (AKI) as well as to monitor a renoprotective strategy. Seventy-two Wistar rats were divided into six groups: sham-operated and rats subjected to 10, 20, 30, 45 and 60 min of bilateral ischemia (I) and 24 h of reperfusion (R). Different times of reperfusion (3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 48, 72, 96 and 120 h) were also evaluated in 30 other rats subjected to 30 min of ischemia. Hsp72 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels were determined in both kidney and urine. Hsp72-specificity as a biomarker to assess the success of a renoprotective intervention was evaluated in rats treated with different doses of spironolactone before I/R. Renal Hsp72 mRNA and protein, as well as urinary Hsp72 levels, gradually increased relative to the extent of renal injury induced by different periods of ischemia quantified by histomorphometry as a benchmark of kidney damage. Urinary Hsp72 increased significantly after 3 h and continued rising until 18 h, followed by restoration after 120 h of reperfusion in accord with histopathological findings. Spironolactone renoprotection was associated with normalization of urinary Hsp72 levels. Accordingly, urinary Hsp72 was significantly increased in patients with clinical AKI before serum creatinine elevation. Our results show that urinary Hsp72 is a useful biomarker for early detection and stratification of AKI. In addition, urinary Hsp72 levels are sensitive enough to monitor therapeutic interventions and the degree of tubular recovery following an I/R insult.
Copyright © 2011 EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Figures
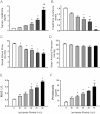
Serum creatinine levels.
Creatinine clearance.
Renal blood flow.
Mean arterial pressure.
Urinary NAG excretion.
Protein excretion.
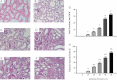
Sham-operated rats.
10 min.
20 min.
30 min.
45 min.
60 min.
Mean cast number per field.
Percentage of tubular affected area.

Total RNA was individually extracted from the renal cortex of all studied groups (n = 5) and Hsp72 mRNA levels were determined by real time RT-PCR.
Renal cortex proteins were individually extracted from three rats of each group, and Hsp72 protein levels were assessed by western blot. Upper inset shows a representative image of the autoradiography of the membrane and the lower graph depicts densitometric analyses of the ratio of Hsp72 to β-actin. *p < 0.05 versus sham-operated rats, £p < 0.05 versus 30 min and ¥p < 0.05 versus 45 min of ischemia group.
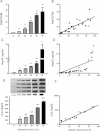
Total RNA was individually extracted from the urine of six rats per group and Hsp72 mRNA levels were determined by real time RT-PCR.
Relationship between mRNA levels and tubular affected area.
Urinary Hsp72 levels assessed by ELISA.
Relationship between urinary Hsp72 levels and the % of tubular affected area.
Urinary Hsp72 levels assessed by WB analysis from four rats of each group.
Relationship between urinary Hsp72 levels detected by WB and tubular injured area. *p < 0.05 versus sham-operated rats, ¤p < 0.05 versus 10 min, €p < 0.05 versus 20 min, £p < 0.05 versus 30 min and ¥p < 0.05 versus 45 min of ischemia group.
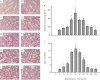
3 h
6 h
9 h
12 h
18 h
24 h
48 h
72 h
96 h and
120 h of reperfusion.
Morphometric quantification of affected tubular area.
Mean cast number per field *p < 0.05 versus sham-operated rats.
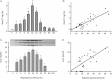
Urinary Hsp72 levels assessed by ELISA.
Relationship between urinary Hsp72 and % of tubular damaged area.
Urinary Hp72 protein levels determined by Western blot.
Relationship between Hsp72 and % of tubular injured area.
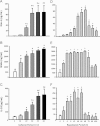
A, B, C. Urinary levels of Kim-1, NGAL, and IL-18 in different degrees of renal injury induced by increasing periods of ischemia (10, 20, 30, 45 and 60 min), respectively.
D, E, F. Urinary concentrations of Kim-1, NGAL and IL-18 after several times of reperfusion (3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 48, 72, 96 and 120 h), respectively.
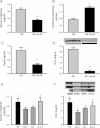
Serum creatinine in I/R group without treatment (gray bar) and rats pre-treated with spironolactone (black bar),
Creatinine clearance,
Urinary Hsp72 assessed by ELISA and
By WB analysis, the inset shows the individual analysis from five individual urines.
Serum creatinine in I/R group and in rats pre-treated with lower doses of spironolactone (10, 5 and 2.5 mg/kg) and
WB analysis of Hsp72 in rats pre-treated with lower doses of spironolactone, the superior inset shows the individual Hsp72 level from five different animals. *p < 0.05 versus I/R group.
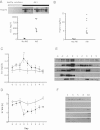
A, B. Hsp72 levels assessed by Western blot and ELISA, respectively, in five healthy kidney donors (▪) and nine patients that were diagnosed with AKI (▴).
C. Serum creatinine from five patients with no evidence of AKI (○) or in five patients with AKI diagnosed with AKIN criteria (•).
D. Urine output from five patients with no evidence of AKI (○) or in five patients with AKI diagnosed with AKIN criteria (•).
E. Daily urinary Hsp72 levels from patients with diagnosed AKI.
F. Daily urinary Hsp72 levels in patients without AKI.
References
-
- Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury: diagnosis and classification of AKI: AKIN or RIFLE. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6:71–73. - PubMed
-
- Csermely P, Soti C, Blatch GL. Chaperones as parts of cellular networks. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;594:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Devarajan P. Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1503–1520. - PubMed
-
- Dieterle F, Perentes E, Cordier A, Roth DR, Verdes P, Grenet O, Pantano S, Moulin P, Wahl D, Mahl, et al. Urinary clusterin, cystatin C, beta2-microglobulin and total protein as markers to detect drug-induced kidney injury. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:463–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

