Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy
- PMID: 21205641
- PMCID: PMC3030664
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1196371
Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy
Abstract
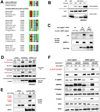
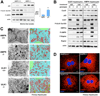
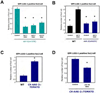
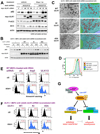
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a conserved sensor of intracellular energy activated in response to low nutrient availability and environmental stress. In a screen for conserved substrates of AMPK, we identified ULK1 and ULK2, mammalian orthologs of the yeast protein kinase Atg1, which is required for autophagy. Genetic analysis of AMPK or ULK1 in mammalian liver and Caenorhabditis elegans revealed a requirement for these kinases in autophagy. In mammals, loss of AMPK or ULK1 resulted in aberrant accumulation of the autophagy adaptor p62 and defective mitophagy. Reconstitution of ULK1-deficient cells with a mutant ULK1 that cannot be phosphorylated by AMPK revealed that such phosphorylation is required for mitochondrial homeostasis and cell survival during starvation. These findings uncover a conserved biochemical mechanism coupling nutrient status with autophagy and cell survival.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cell biology. Why starving cells eat themselves.Science. 2011 Jan 28;331(6016):410-1. doi: 10.1126/science.1201691. Science. 2011. PMID: 21273476 No abstract available.
-
AMPK activates autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1.Circ Res. 2011 Apr 1;108(7):787-8. doi: 10.1161/RES.0b013e3182194c29. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21454792 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

