Olfaction in Parkin heterozygotes and compound heterozygotes: the CORE-PD study
- PMID: 21205674
- PMCID: PMC3034420
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820882aa
Olfaction in Parkin heterozygotes and compound heterozygotes: the CORE-PD study
Abstract
Background: While Parkinson disease (PD) is consistently associated with impaired olfaction, one study reported better olfaction among Parkin mutation carriers than noncarriers. Whether olfaction differs between Parkin mutation heterozygotes and carriers of 2 Parkin mutations (compound heterozygotes) is unknown.
Objective: To assess the relationship between Parkin genotype and olfaction in PD probands and their unaffected relatives.
Methods: We administered the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT) to 44 probands in the Consortium on Risk for Early-Onset Parkinson Disease study with PD onset ≤50 years (10 Parkin mutation heterozygotes, 9 compound heterozygotes, 25 noncarriers) and 80 of their family members (18 heterozygotes, 2 compound heterozygotes, 60 noncarriers). In the probands, linear regression was used to assess the association between UPSIT score (outcome) and Parkin genotype (predictor), adjusting for covariates. Among family members without PD, we compared UPSIT performance in heterozygotes vs noncarriers using generalized estimating equations, adjusting for family membership, age, gender, and smoking.
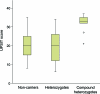
Results: Among probands with PD, compound heterozygotes had higher UPSIT scores (31.9) than heterozygotes (20.1) or noncarriers (19.9) (p < 0.001). These differences persisted after adjustment for age, gender, disease duration, and smoking. Among relatives without PD, UPSIT performance was similar in heterozygotes (32.5) vs noncarriers (32.4), and better than in heterozygotes with PD (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: Olfaction is significantly reduced among Parkin mutation heterozygotes with PD but not among their heterozygous relatives without PD. Compound heterozygotes with PD have olfaction within the normal range. Further research is required to assess whether these findings reflect different neuropathology in Parkin mutation heterozygotes and compound heterozygotes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Olfaction in Parkin-associated Parkinson disease: another enigma.Neurology. 2011 Jan 25;76(4):312-3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820882ee. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21205673 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, et al. Mutations in the Parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 1998;392:605–608 - PubMed
-
- Hedrich K, Eskelson C, Wilmot B, et al. Distribution, type, and origin of Parkin mutations: review and case studies. Mov Disord 2004;19:1146–1157 - PubMed
-
- Lucking CB, Durr A, Bonifati V, et al. Association between early-onset Parkinson's disease and mutations in the Parkin gene: French Parkinson's Disease Genetics Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1560–1567 - PubMed
-
- Hedrich K, Marder K, Harris J, et al. Evaluation of 50 probands with early-onset Parkinson's disease for Parkin mutations. Neurology 2002;58:1239–1246 - PubMed
-
- Abbas N, Lucking CB, Ricard S, et al. A wide variety of mutations in the Parkin gene are responsible for autosomal recessive parkinsonism in Europe: French Parkinson's Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson's Disease. Hum Mol Genet 1999;8:567–574 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
