From the Cover: Bacterial flagellum as a propeller and as a rudder for efficient chemotaxis
- PMID: 21205908
- PMCID: PMC3038696
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1011953108
From the Cover: Bacterial flagellum as a propeller and as a rudder for efficient chemotaxis
Abstract
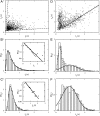
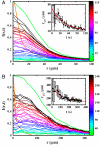
We investigate swimming and chemotactic behaviors of the polarly flagellated marine bacteria Vibrio alginolyticus in an aqueous medium. Our observations show that V. alginolyticus execute a cyclic, three-step (forward, reverse, and flick) swimming pattern that is distinctively different from the run-tumble pattern adopted by Escherichia coli. Specifically, the bacterium backtracks its forward swimming path when the motor reverses. However, upon resuming forward swimming, the flagellum flicks and a new swimming direction is selected at random. In a chemically homogeneous medium (no attractant or repellent), the consecutive forward t(f) and backward t(b) swimming times are uncorrelated. Interestingly, although t(f) and t(b) are not distributed in a Poissonian fashion, their difference Δt = |t(f) - t(b)| is. Near a point source of attractant, on the other hand, t(f) and t(b) are found to be strongly correlated, and Δt obeys a bimodal distribution. These observations indicate that V. alginolyticus exploit the time-reversal symmetry of forward and backward swimming by using the time difference to regulate their chemotactic behavior. By adopting the three-step cycle, cells of V. alginolyticus are able to quickly respond to a chemical gradient as well as to localize near a point source of attractant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Reverse and flick: Hybrid locomotion in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 15;108(7):2635-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019199108. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21289282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Berg HC, Anderson RA. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973;245:380–382. - PubMed
-
- Silverman M, Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974;249:73–74. - PubMed
-
- Berg HC, Brown DA. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972;239:500–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

