Association of a microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry with pathogenesis and outcome of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 21205967
- PMCID: PMC3690301
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2010.1919
Association of a microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry with pathogenesis and outcome of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Erratum in
-
Incorrect Immunoblot in Figure.JAMA. 2025 Jul 8;334(2):184. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.9581. JAMA. 2025. PMID: 40489316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Context: Chromosomal abnormalities (namely 13q, 17p, and 11q deletions) have prognostic implications and are recurrent in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), suggesting that they are involved in a common pathogenetic pathway; however, the molecular mechanism through which chromosomal abnormalities affect the pathogenesis and outcome of CLL is unknown.
Objective: To determine whether the microRNA miR-15a/miR-16-1 cluster (located at 13q), tumor protein p53 (TP53, located at 17p), and miR-34b/miR-34c cluster (located at 11q) are linked in a molecular pathway that explains the pathogenetic and prognostic implications (indolent vs aggressive form) of recurrent 13q, 17p, and 11q deletions in CLL.
Design, setting, and patients: CLL Research Consortium institutions provided blood samples from untreated patients (n = 206) diagnosed with B-cell CLL between January 2000 and April 2008. All samples were evaluated for the occurrence of cytogenetic abnormalities as well as the expression levels of the miR-15a/miR-16-1 cluster, miR-34b/miR-34c cluster, TP53, and zeta-chain (TCR)-associated protein kinase 70 kDa (ZAP70), a surrogate prognostic marker of CLL. The functional relationship between these genes was studied using in vitro gain- and loss-of-function experiments in cell lines and primary samples and was validated in a separate cohort of primary CLL samples.
Main outcome measures: Cytogenetic abnormalities; expression levels of the miR-15a/miR-16-1 cluster, miR-34 family, TP53 gene, downstream effectors cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1) (CDKN1A) and B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 binding component 3 (BBC3), and ZAP70 gene; genetic interactions detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation.
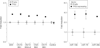
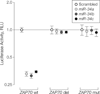
Results: In CLLs with 13q deletions the miR-15a/miR-16-1 cluster directly targeted TP53 (mean luciferase activity for miR-15a vs scrambled control, 0.68 relative light units (RLU) [95% confidence interval {CI}, 0.63-0.73]; P = .02; mean for miR-16 vs scrambled control, 0.62 RLU [95% CI, 0.59-0.65]; P = .02) and its downstream effectors. In leukemic cell lines and primary CLL cells, TP53 stimulated the transcription of miR-15/miR-16-1 as well as miR-34b/miR-34c clusters, and the miR-34b/miR-34c cluster directly targeted the ZAP70 kinase (mean luciferase activity for miR-34a vs scrambled control, 0.33 RLU [95% CI, 0.30-0.36]; P = .02; mean for miR-34b vs scrambled control, 0.31 RLU [95% CI, 0.30-0.32]; P = .01; and mean for miR-34c vs scrambled control, 0.35 RLU [95% CI, 0.33-0.37]; P = .02).
Conclusions: A microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry is associated with CLL pathogenesis and outcome. This mechanism provides a novel pathogenetic model for the association of 13q deletions with the indolent form of CLL that involves microRNAs, TP53, and ZAP70.
Figures




Comment in
-
Unraveling the molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: dissecting a microRNA regulatory network.JAMA. 2011 Jan 5;305(1):95-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1940. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21205973 No abstract available.
-
CLL pathogenesis: novel microRNA/ TP53 feedback circuitry.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011 Mar;8(3):125. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21480561 No abstract available.
References
-
- Call TG, Phyliky RL, Noel P, et al. Incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in Olmsted County, Minnesota: 1935 through 1989, with emphasis on changes in initial stage at diagnosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994 Apr;69(4):323–328. - PubMed
-
- Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1975 Aug;46(2):219–234. - PubMed
-
- Binet JL, Lepoprier M, Dighiero G, et al. A clinical staging system for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: prognostic significance. Cancer. 1977 Aug;40(2):855–864. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000 Dec 28;343(26):1910–1916. - PubMed
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 2005 Feb 24;352(8):804–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

