Three-dimensional visualization of subdural electrodes for presurgical planning
- PMID: 21206319
- PMCID: PMC4339031
- DOI: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e31820783ba
Three-dimensional visualization of subdural electrodes for presurgical planning
Abstract
Background: Accurate localization and visualization of subdural electrodes implanted for intracranial electroencephalography in cases of medically refractory epilepsy remains a challenging clinical problem.
Objective: We introduce a technique for creating accurate 3-dimensional (3D) brain models with electrode overlays, ideal for resective surgical planning.
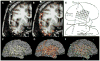
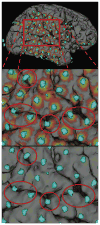
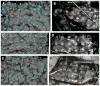
Methods: Our procedure uses postimplantation magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomographic (CT) imaging to create 3D models of compression-affected brain combined with intensity-thresholded CT-derived electrode models using freely available software. Footprints, or "shadows," beneath electrodes are also described for better visualization of sulcus-straddling electrodes. Electrode models were compared with intraoperative photography for validation.
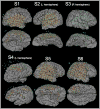
Results: Realistic representations of intracranial electrode positions on patient-specific postimplantation MRI brain renderings were reliably created and proved accurate when compared with photographs. Electrodes placed interhemispherically were also visible with our rendering technique. Electrode shadows were useful in locating electrodes that straddle sulci.
Conclusion: We present an accurate method for visualizing subdural electrodes on brain compression effected 3D models that serves as an ideal platform for surgical planning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
3D visualization of subdural electrode shift as measured at craniotomy reopening.Epilepsy Res. 2011 Mar;94(1-2):102-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Epilepsy Res. 2011. PMID: 21334178 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative computed tomography for intracranial electrode implantation surgery in medically refractory epilepsy.J Neurosurg. 2015 Mar;122(3):526-31. doi: 10.3171/2014.9.JNS13919. Epub 2014 Oct 31. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25361483
-
Visualization of subdural electrodes with fusion CT scan/MRI during neuronavigation-guided epilepsy surgery.J Clin Neurosci. 2010 Apr;17(4):511-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2009.06.038. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Clin Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20122830 Clinical Trial.
-
Neuronavigation applied to epilepsy monitoring with subdural electrodes.Neurosurg Focus. 2008 Sep;25(3):E21. doi: 10.3171/FOC/2008/25/9/E21. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. PMID: 18759623 Review.
-
Cerebral Angiography for Multimodal Surgical Planning in Epilepsy Surgery: Description of a New Three-Dimensional Technique and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2015 Aug;84(2):358-67. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.03.028. Epub 2015 Mar 25. World Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25819527 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of Subdural Electrode Shift Between Initial Implantation, Postimplantation Computed Tomography, and Subsequent Resection Surgery.Oper Neurosurg. 2019 Jan 1;16(1):9-19. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy050. Oper Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 29617890 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting seizure onset zones from interictal intracranial EEG using functional connectivity and machine learning.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17801. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02679-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404720 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical registration of intracranial electrodes. Robust model-based localization and deformable smooth brain-shift compensation methods.J Neurosci Methods. 2024 Apr;404:110056. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2024.110056. Epub 2024 Jan 14. J Neurosci Methods. 2024. PMID: 38224783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localization of dense intracranial electrode arrays using magnetic resonance imaging.Neuroimage. 2012 Oct 15;63(1):157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.039. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22759995 Free PMC article.
-
3D visualization of subdural electrode shift as measured at craniotomy reopening.Epilepsy Res. 2011 Mar;94(1-2):102-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Epilepsy Res. 2011. PMID: 21334178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luders H, Awad I, Burgess R, Wyllie E, Van Ness P. Subdural electrodes in the presurgical evaluation for surgery of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res Suppl. 1992;5(suppl):147–156. - PubMed
-
- Engel J, Jr, Henry TR, Risinger MW, et al. Presurgical evaluation for partial epilepsy: relative contributions of chronic depth-electrode recordings versus FDG-PET and scalp-sphenoidal ictal EEG. Neurology. 1990;40(11):1670–1677. - PubMed
-
- Jayakar P, Duchowny M, Resnick TJ. Subdural monitoring in the evaluation of children for epilepsy surgery. J Child Neurol. 1994;9(Suppl 2):61–66. - PubMed
-
- Behrens E, Zentner J, van Roost D, Hufnagel A, Elger CE, Schramm J. Subdural and depth electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1994;128(1–4):84–87. - PubMed
-
- Luders H, Lesser RP, Dinner DS, Hahn JF, Salanga V, Morris HH. The second sensory area in humans: evoked potential and electrical stimulation studies. Ann Neurol. 1985;17(2):177–184. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

