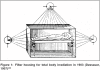
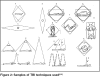
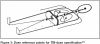
Whole body radiotherapy: A TBI-guideline
- PMID: 21206634
- PMCID: PMC3003894
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.25664
Whole body radiotherapy: A TBI-guideline
Abstract
Total Body Irradiation (TBI) is one main component in the interdisciplinary treatment of widely disseminated malignancies predominantly of haematopoietic diseases. Combined with intensive chemotherapy, TBI enables myeloablative high dose therapy and immuno-ablative conditioning treatment prior to subsequent transplantation of haematopoietic stem cells: bone marrow stem cells or peripheral blood progenitor stem cells. Jointly prepared by DEGRO and DGMP, the German Society of Radio-Oncology, and the German Association of Medical Physicists, this DEGRO/DGMP-Leitlinie Ganzkoerper-Strahlenbehandlung - DEGRO/DGMP Guideline Whole Body Radiotherapy, summarises the concepts, principles, facts and common methods of Total Body Irradiation and poses a set of recommendations for reliable and successful application of high dose large-field radiotherapy as essential part of this interdisciplinary, multi-modality treatment concept. The guideline is geared towards radio-oncologists, medical physicists, haematooncolo-gists, and all contributing to Whole Body Radiotherapy. To guide centres intending to start or actualise TBI criteria are included. The relevant treatment parameters are defined and a sample of a form is given for reporting TBI to international registries.
Keywords: TBI; dosimetry; guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- VanDyk J, Galvin JM, Glasgow GW, Podgorsak E, editors. AAPM report No. 17. The physical aspects of total and half body photon irradiation. New York: American Inst Phys; 1986.
-
- VanDyk J, Keane TJ, Kan S, Rider WD, Fryer CJ. Radiation pneumonitis following large single dose irradiation: Re-evaluation based on absolute dose to lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1981;7:461–7. - PubMed
-
- Glasgow GP. The dosimetry of fixed, single source hemibody and total body irradiators. Med Phys. 1982;9:311–23. - PubMed
-
- VanDyk J. Wright A, Boyer AL, editors. Whole and partial body radiotherapy: physical considerations. Med Phys Monogr Ser. 1983;9:403–26.
-
- Shank B. Techniques of magna-field irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1983;9:1925–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources